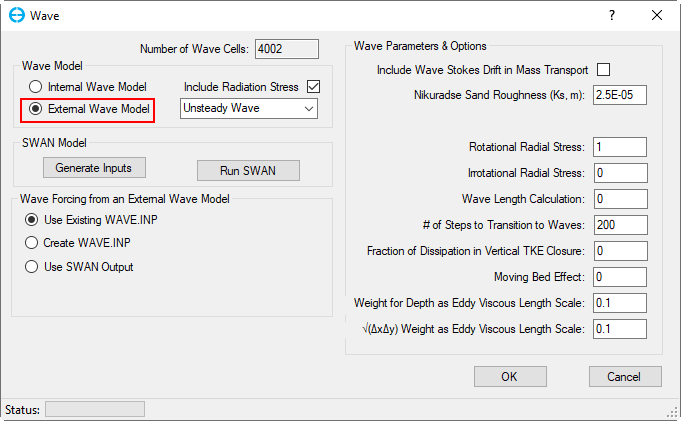
External Wave Model (EEMS10.2)
EE currently supports the use of SWAN as the external wave model. SWAN (Simulating Waves Nearshore) as a third-generation wave model is suitable for wind-generated surface gravity wave simulation in coastal, lakes, and estuaries. EE provides several options to ensure a smooth transition between EE and SWAN, users can either use EE to generate a new SWAN model and run it or import an existing SWAN model result.
The Steady Wave /Unsteady Wave option corresponds to the types of waves being imported into the EFDC model. The steady wave option means that the waves are not changing with time so the EE will not read the WAVETIME.INP file. The unsteady wave option does require the WAVETIME.INP input file. The setting in the frame reflects the way the user has imported the external waves.
Figure 1 Waves Module: External Wave.
SWAN Model
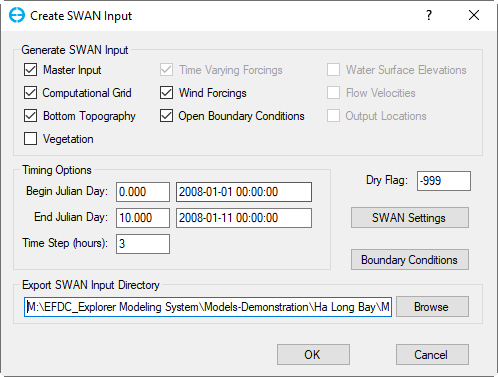
Generate Inputs: Click on this button to generate input file for the SWAN model, the Create SWAN Input form pops up as shown in Figure 2. There are several optional check-boxes in Generate SWAN Input
Time Options: Define begin day, end day, and time step for the SWAN model, this time period should be in the range of the EFDC Model running time.
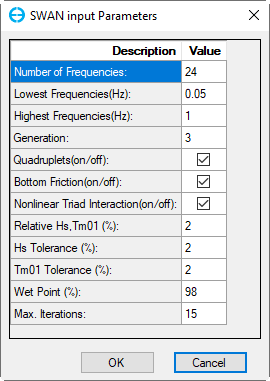
SWAN Settings: Click on this button to show the SWAN settings as shown in Figure 3.
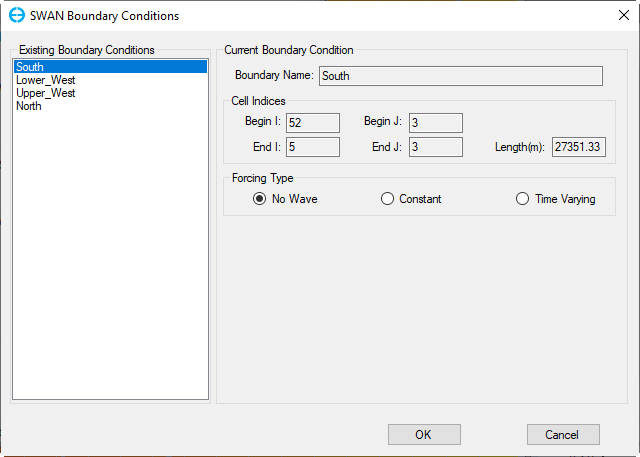
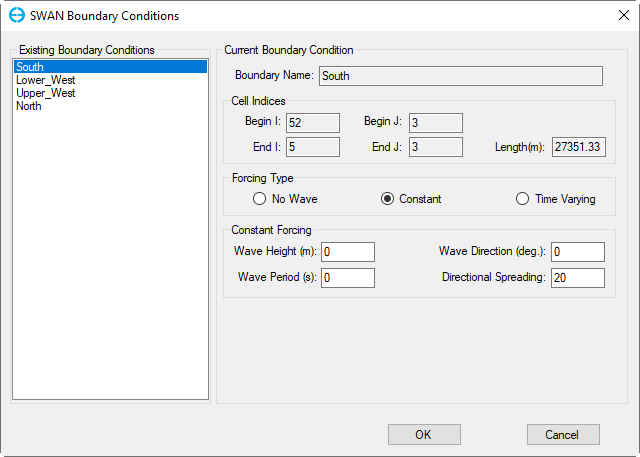
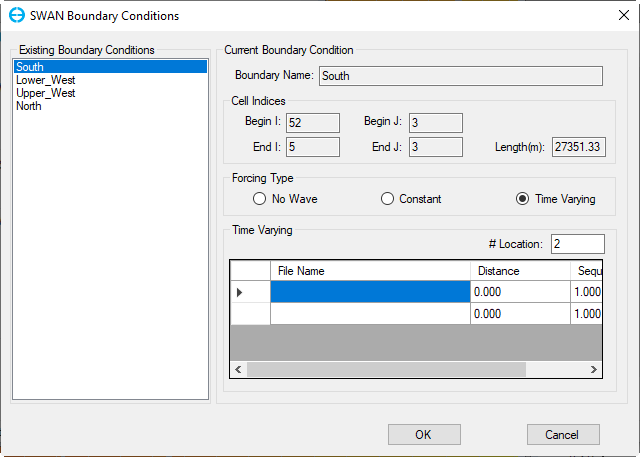
If the check-box Open Boundary Conditions checked, then the button Boundary Conditions button is enabled, click on that button, form of SWAN Boundary Conditions appears as shown in Figure 4. There are three options to set Forcing Type from existing boundary conditions of the model as No wave (Figure 4), Constant (Figure 5), Time Varying (Figure 6).
Export SWAN Input Directory: As default, the SWAN input file (swan_inp.swn) will be created and saved in the #analysis folder.
Figure 2 Create SWAN Model Input.
Figure 3 SWAN Input Parameters.
Figure 4 SWAN Boundary Conditions: No Wave.
Figure 5 SWAN Boundary Conditions: Constant.
Figure 6 SWAN Boundary Conditions: Time Varying.
Run SWAN
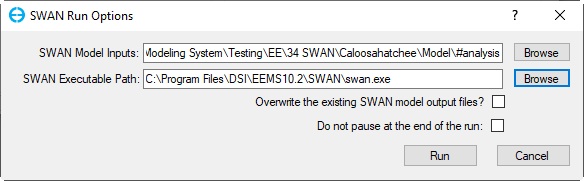
After the SWAN input file has been created, the user now can run SWAN by clicking on Run SWAN button (Figure 1), the SWAN Run Options form pops up as shown in Figure 7.
SWAN Model Input: Click the Browse button to browse to the input file in the #analysis folder (swan_inp.swn)
SWAN Executable Path: Click the Browse button to browse to the executable file in SWAN folder of the EEMS installation folder.
Finally, click Run button in Figure 7 to run SWAN model. Figure 8 shows a running SWAN model window.
Figure 7 Run SWAN model.
Figure 8 SWAN model Running.
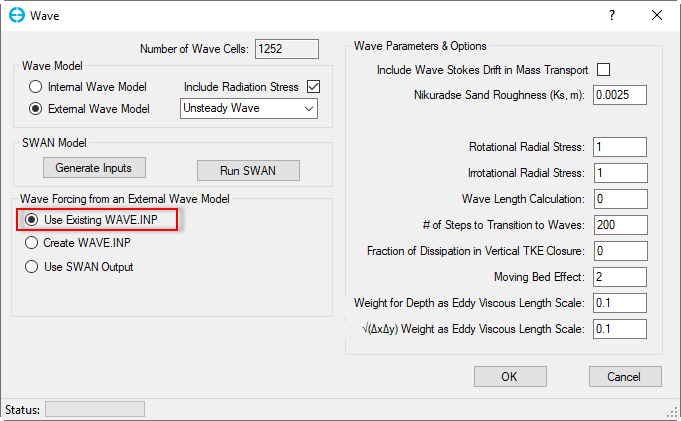
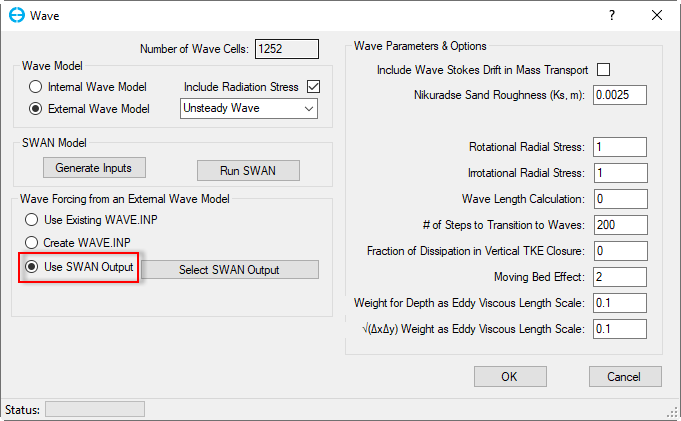
Wave Forcing from an External Wave Model:
Use Existing WAVE.INP: If the user already has a WAVE.INP file and this file must be located in the model folder then the wave data is imported first time by checking the Use Existing WAVE.INP checkbox as shown in Figure 9.
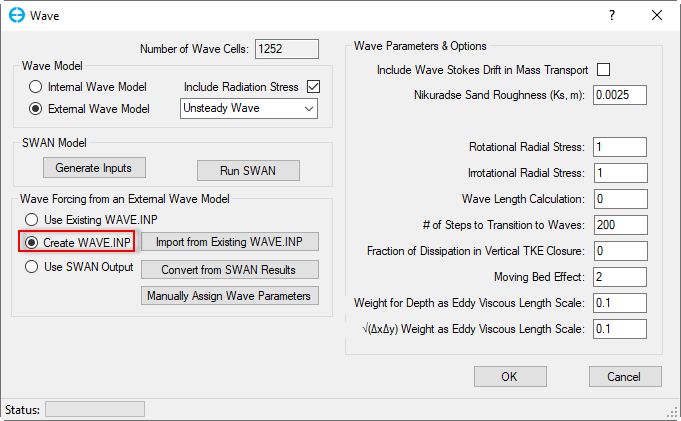
Create WAVE.INP: The user can create wave.inp file by using this option. When this option is selected, three sub-options will appear as shown in Figure 10. They include Import from Existing WAVE.INP, Convert from SWAN results and Manually Assign Wave Parameters. These three buttons are described below:
Figure 9 Wave forcing from external wave model: Use Existing WAVE.INP
Figure 10 Wave forcing from external wave model: Create WAVE.INP
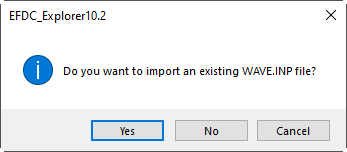
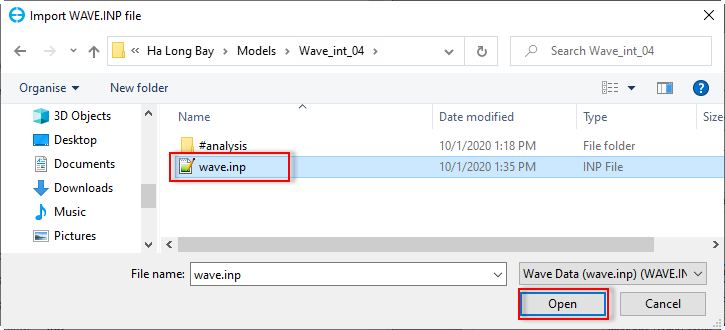
- Import from Existing WAVE.INP: EE imports an available WAVE.INP file from another project into the current project (Note: two projects have exactly the same grids). When clicking on this button, a message will be popped up as shown in Figure 11. Click Yes button to proceed with the process. The Import WAVE.INP file form will appear, select the wave.inp then click Open button as shown in Figure 12. After clicking Open button, it comes back to the Wave form. Note that the user needs to save the model again then the wave.inp file for the current model will be created.
Figure 11 Message confirmation to import WAVE.INP
Figure 12 Import WAVE.INP file.
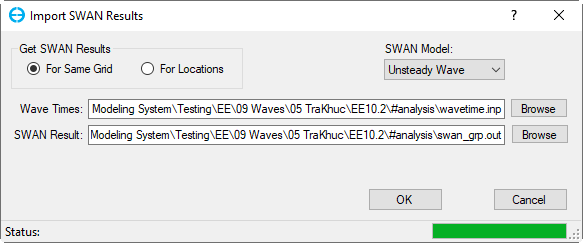
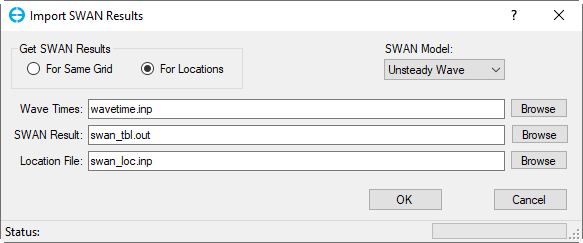
- Convert from SWAN results: EE will create wave.inp file by converting from SWAN output. Selecting this option, the Import SWAN Results form will appear as shown in Figure 13. The user must define the type of SWAN model (Steady or Unsteady Wave) from the drop-down list. In the Get SWAN Results frame, the user selects For Same Grid option (if the SWAN model and EFDC model have the same grid of model domain) or For Locations option ( if the SWAN model and EFDC model have a different grid of model domain) then browse to wave time file (wavetime.inp) and SWAN output file (swan_grp.out). In case the For Locations option is selected, the user needs to browse to table file (swan_tbl.out) and location file (swan_loc.inp) as shown Figure 14. Finally, click OK button to come back the Wave form. Note that the user needs to save the model again then the wave.inp file for the current model will be created.
Figure 13 Import SWAN Results: For Same Grid.
Figure 14 Import SWAN Results: For Locations.
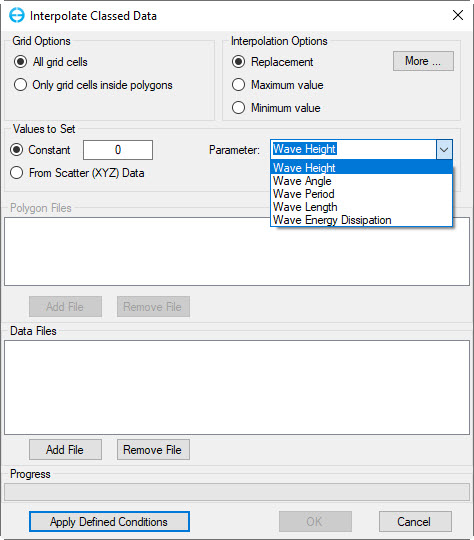
- Manually Assign Wave Parameters: This option is not advised to be used due to the longer time required to prepare the input data. When this option is selected, an Interpolate Classed Data form will appear as shown in Figure 15. In the Grid Options frame, select one of two options: All grid cells or Only grid cells inside polygon (when this option is selected, the Add File button in the Polygon Files frame below will be enabled). There are three options for Interpolation Options frame (Replacement, Max, and Min values). In the Values to Set frame, select Constant if the user wants to set wave parameters in grid cells with a constant value. Select From Scatter (XYZ) Data if the user has a wave data file ( the file has three columns, the two first columns are coordinates, the third column is wave parameter value). When this option is selected, the Add File of Data File frame will be enabled). Next, select wave parameter from the drop-down list of the Parameters. Finally, Click Apply Defined Condition button then OK button. Note that the user needs to save the model again to create the wave.inp file for the current model.
Figure 15 Interpolate Classed Data form.
Use SWAN Output: EE will use the SWAN output directly instead of creating wave.inp. When this option is selected, the Select SWAN Output button will appear as shown in Figure 16. Click this button, the Import SWAN Results form will be displayed as shown in Figure 13. Usage of options on this form is described above. After the configuration is completed, the EFDC.INP file will be updated. EFDC+ will then look for the appropriate files in the root level of the project directory.
Figure 16 Wave forcing from external wave model: Use SWAN Output.