...
Disable Ice Model
External Ice Time Series (ISER & ICEMAP)
Specified ON/OFF Ice Cover
Heat Coupled Ice Model
Heat Coupled Ice Model with Frazil Transport
Figure 1. Temperature Parameters - Ice moduletab.
The application and operation of each of these options are explained in the following sections.
...
For the option ISICE=1, EFDC uses the ISER.INP to read time and ice thickness for externally specified ice cover. However, the ice thickness is not actually used by EFDC. The time series of a flag (0 – off, 1 – on) in the ISER is interpolated between the earlier and later times to the current time. If the flag is > 0.5 then ice is on, and if the flag is < 0.5, then ice is off. The ICEMAP.INP is used for the weighting coefficients of ice thickness in case more than one time series is given in the ISER.INP. ICEMAP with the NISER weightings (the number of ice series) when NISER>1 can be both read and written.
Figure 2. Ice Parameters: External Ice Time Series.
...
This option is effectively a global toggle so that ice may be turned on or off over the whole domain. The time series file that populates this option lists a date and toggle on and toggle off with the input file ISTAT.INP.
...
Figure 3. Ice Parameters: Specified ON/OFF Ice Cover.
...
Currently, the ice sub-model in EFDC+ is only an ice cover model and not an ice and snow cover model. The snow cover would account for snow on top of the ice and is expected to be added for an upcoming release. The ice cover model allows light to be attenuated through the ice. The solar radiation absorption is accounted for in this process. To implement this in EFDC, routines such as CALQVS and CALHEAT were modified. CALPUV was also updated so that the bed heat is handled when the elevation is below the bottom of the cell.
Figure 4 shows the default values of the ice parameters that are required to simulate ice in EFDC+ model. A checkbox is provided for the Use Ryan Harleman Wind Function option if desired.
...
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Figure 4. Ice Parameters: Heat Coupled Ice Model.
...
In addition to the modification to the EFDC subroutines outlined for ISICE =3, a new routine, CALTRANICE, is created to simulate frazil ice as a concentration.
Figure 5. Ice Parameters: Use Heat Coupled Ice Model with Frazil Ice Transport.
...
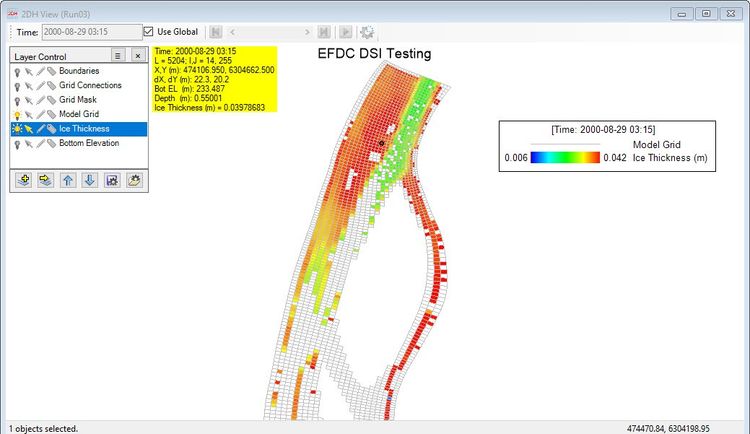
Output from the ice sub-model can be displayed in a number of ways in EE. A 2D plan view of the ice thickness or temperature may be viewed by selecting 2DH View and then add layer Thermal/Ice | Ice Thickness. Figure 6 shows an example of frazil ice formation in a river in Alberta, Canada. Note that initially, ice forms on the river banks where depths are shallower and flow is lower.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Figure 6. Ice Sub model: 2DH View frazil ice thickness.
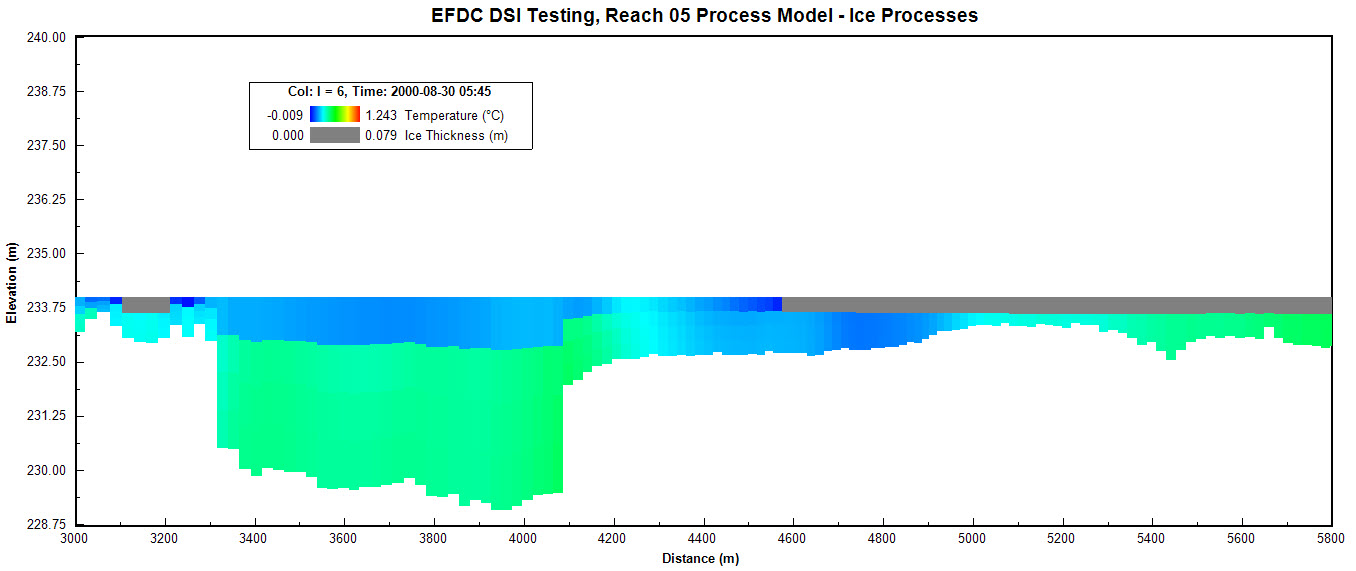
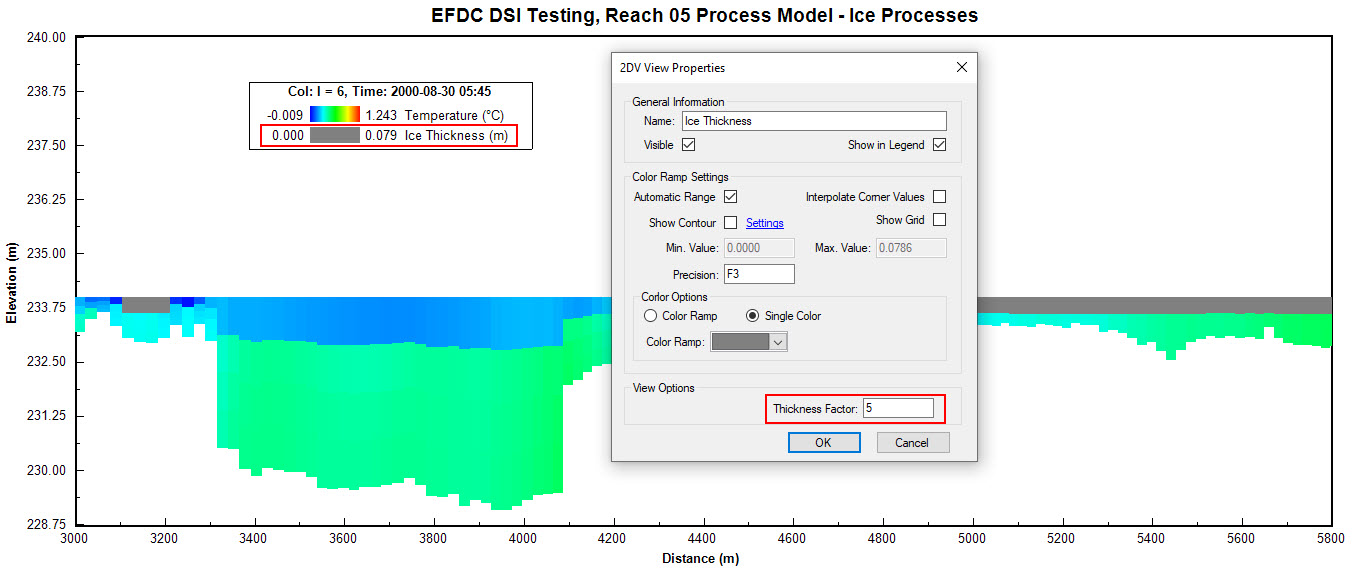
The user can also visualize ice on the water column in the 2DV View tool. This displays a solid grey color as shown in Figure 7. The vertical exaggeration of the ice layer can be modified by RMC on Ice Thickness | Properties and change the Thickness Factor to show it more clearly as shown in Figure 8.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Figure 7. Ice Sub model: 2DV View ice cover and WC temperature.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Figure 8. Ice Sub model: 2DV View Properties.