Table of Contents
1 Introduction
This tutorial document will guide you how to setup a coastal hydrodynamic model by using the EFDC_Explorer (EE). It will cover preparation of the necessary input files for the EFDC model and visualization of the output by using the EFDC_Explorer (EE) Software.
The data used for this tutorial are from Tra Khuc Estuary in Vietnam. All files for this tutorial are found in Data folder downloadable from the EEMS website.
Before going to each session, let us first introduce the EE main form in order to better understand our explanation hereafter. 2381073 . Figure 1 is the main form of EFDC_Explorer or EE User Interface. The functions of individual icons are described in Knowledge Base.
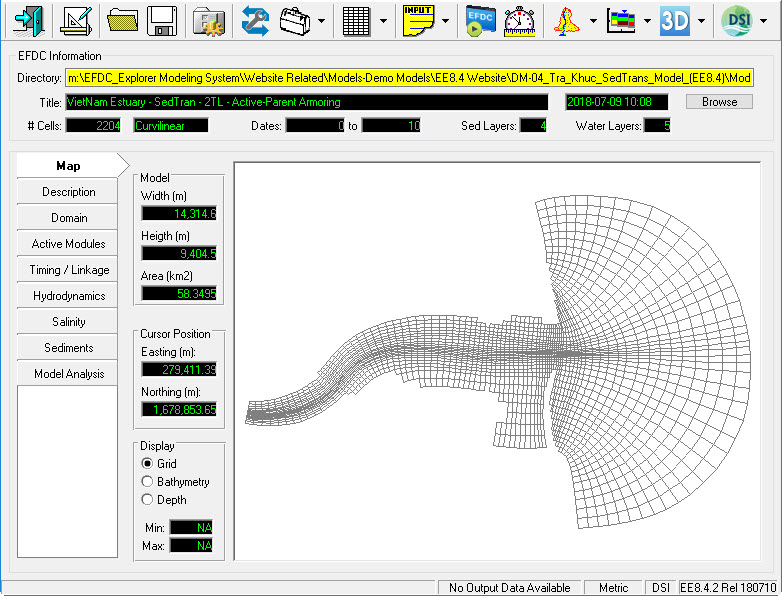
Figure 1 EFDC Explorer main form.
2 Create a New Grid
This section will guide you in how to create a new simple gird with EFDC_Explorer. For a complicated grid the user is recommended to use specialized grid generation software such as CVLGrid.
Tra Khuc Estuary in Quang Ngai province, Vietnam is chosen as the example of building a 3D coastal model in EE.
The gird generation process includes following steps:
- Open EE
- Click Generate New Model icon as
 on the main menu of EE interface. Then Generate EFDC Model frame appears shown in 2381073Figure 2
on the main menu of EE interface. Then Generate EFDC Model frame appears shown in 2381073Figure 2 - Select CVLGrid in the Grid Type. The user should click the Browse button to select grid file name as Trakhuc.cvl in Grid folder sas as shown in 2381073 Figure 2. In the other hand, EE also supports the user to import various format of grid file with the option Import Grid.
- Click Generate button in 2381073 to Figure 2 to finish. A dialog will pop up to show the grid information (see 2381073see Figure 3).
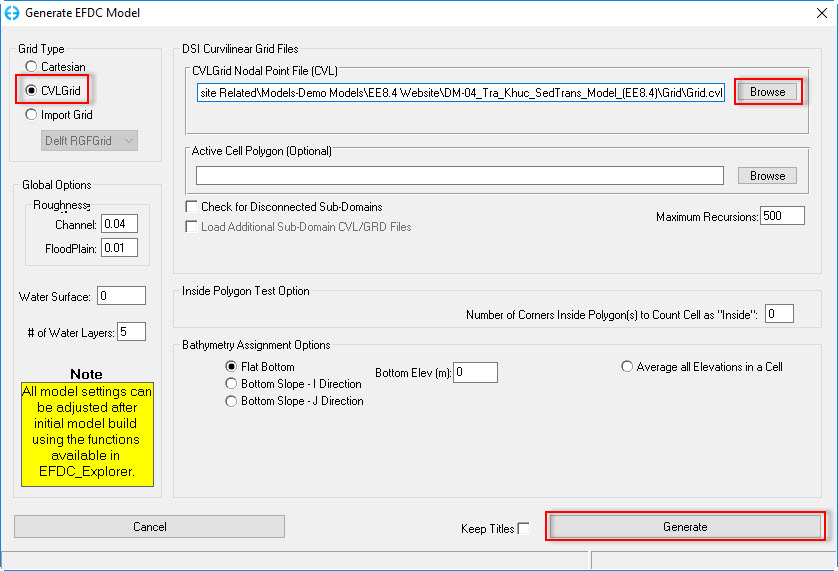
Figure 2 Generate EFDC Model form.
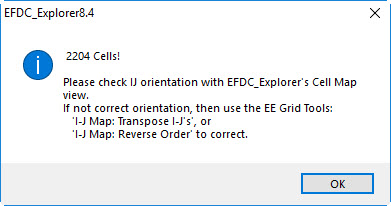
Figure 3 New created grid information.
5. Save the model by selecting this button  and create a new directory as shown in 2381073 Figure 4.
and create a new directory as shown in 2381073 Figure 4.
Figure 4 New model saved.
3 Assigning the Initial Conditions
This section will guide you in how to assign the initial conditions such as the bathymetry, water level and bottom roughness.
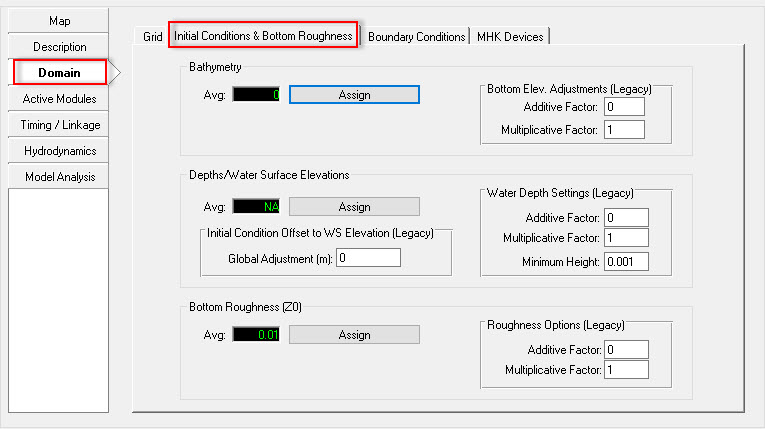
Figure 5 Assigning the initial conditions.
3.1 Assigning the Initial Bottom Conditions
- Select the Domain/Initial Conditions & Bottom Roughness and click the Assign button (see 2381073 Figure 5).
- A polyline file is used to define the area to assign the bathymetry data. To assign this browse in the Poly File form to "Domain.p2d".
- Next browse to the bathymetry data file in the Data File form. This bathymetry file is simply a general xyz format.
- There are a number of options for the for user to modify the assigned. In this case, we choose in the Bathymetry Assignment Options we select Interpolated Data and Both. This will take the nearest neighbor data points to interpolate for the cells where there is no data coverage.
- Click the Apply button to take the effect before hitting the Done button (see 2381073see Figure 6)
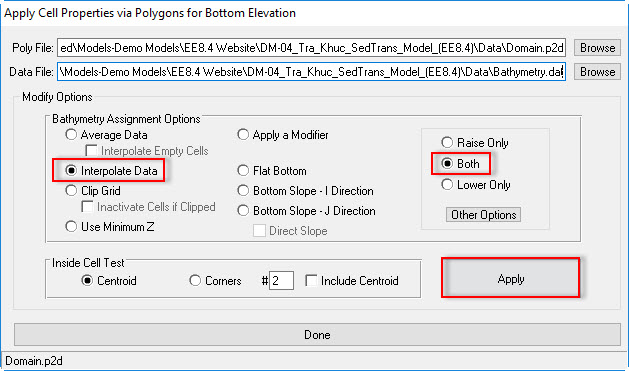
Figure 6 Assigning the bathymetry.
3.2 Assigning the Depth/Water Surface Elevations
The next step is to assign the initial depth or water surface elevations. There are two options for setting the surface water elevation which are Use Constant and Use Point Measurements/Gridded Data.
- Click Assign button
- Browse in the Poly File form to "Domain.p2d"
- Next, browse to the water surface elevation data file "IC_WSEL.dat" in the Data File form.
- Checked on Use Point Measurements/Gridded Data
- The user click Apply button then click Done button to finish.
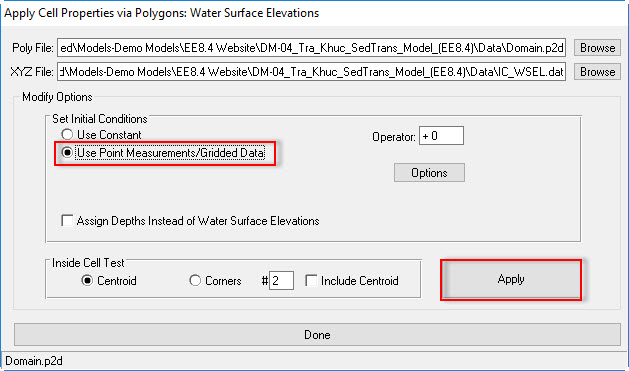
Figure 7 Assigning water surface elevation.
3.3 Assigning the Bottom Roughness (Z0)
- Click the Assign button in the Bottom Roughness (Z0) box (2381073Figure 5).
- Browse in the Poly File form to "Domain.p2d"
- Next, browse to the bottom roughness data file "IC Bot Roughness.dat" in Data folder in the Data File form.
- Checked on Use Point Measurements/Gridded Data
- Click the Apply button before hitting the Done button as shown in 2381073 Figure 8.
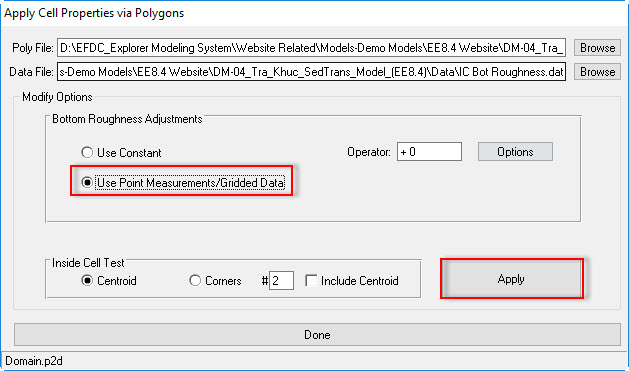
Figure 8 Assigning bottom roughness.
4 Assigning the Boundary Conditions
This section will guide you how to prepare for the boundary conditions and assign it to the model cell configuration. In this coastal case there are two flow boundaries; one is river discharge from the upstream and the other is tidal level. Thus, we should prepare two time series of inflow and tidal level boundaries for this particular case. In order to set a boundary time series the steps outlined below should be taken.
4.1 Preparing the Flow Boundary.
- Select the Domain/Boundary Conditions. (See 2381073 Figure 9).
- Click to the E button
 which is next to Flow to edit the flow boundary. (2381073Figure 9)
which is next to Flow to edit the flow boundary. (2381073Figure 9) - Enter the Number of Series into the box which in this case is 1.
- Give a Title for associated time series, in this case "River".
- Click Import Data button, browse to "BC_Flow.dat" file in Data folder
- Select EE DAT or WQ Data format then click OK button. (See 2381073 Figure 10).
- Enter "-1" in Import Data form then click OK button. (See 2381073 Figure 11).
Click to the Current button  to view the current time series. If there are a number of layers then check Sum Layers to show total flow. (See 2381073 Figure 12). Close timeseries data plot
to view the current time series. If there are a number of layers then check Sum Layers to show total flow. (See 2381073 Figure 12). Close timeseries data plot
Click OK button in Data Series: Flow form to finish editing the boundary time series.
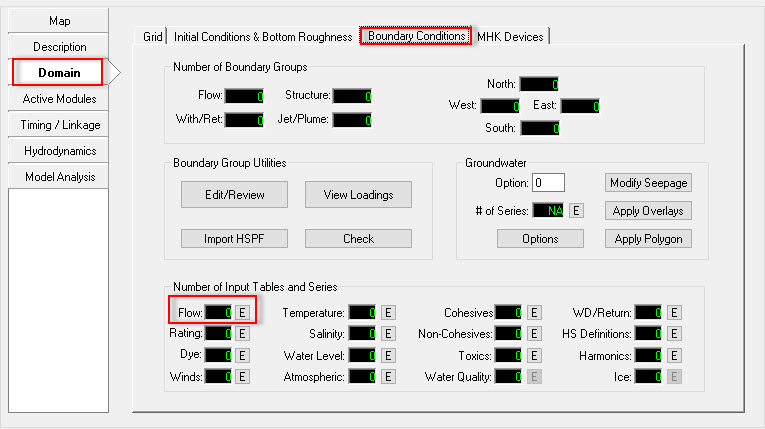
Figure 9 Assigning flow boundary conditions.
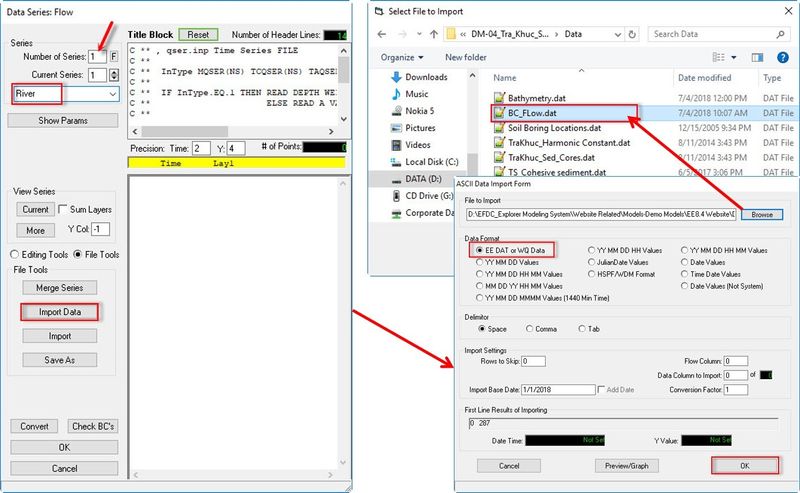
Figure 10 Editing the boundary time series (01).
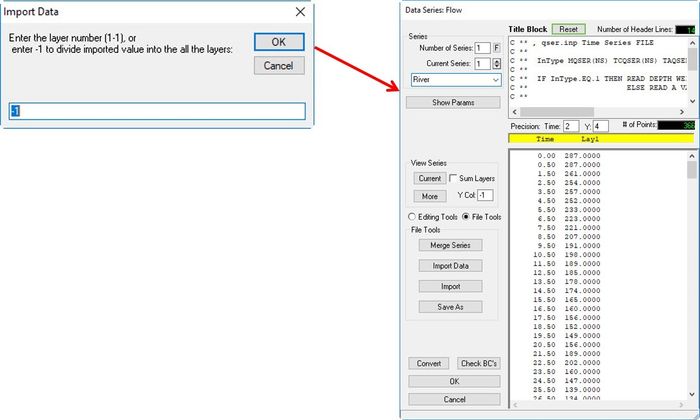
Figure 11 Editing the boundary time series (02).
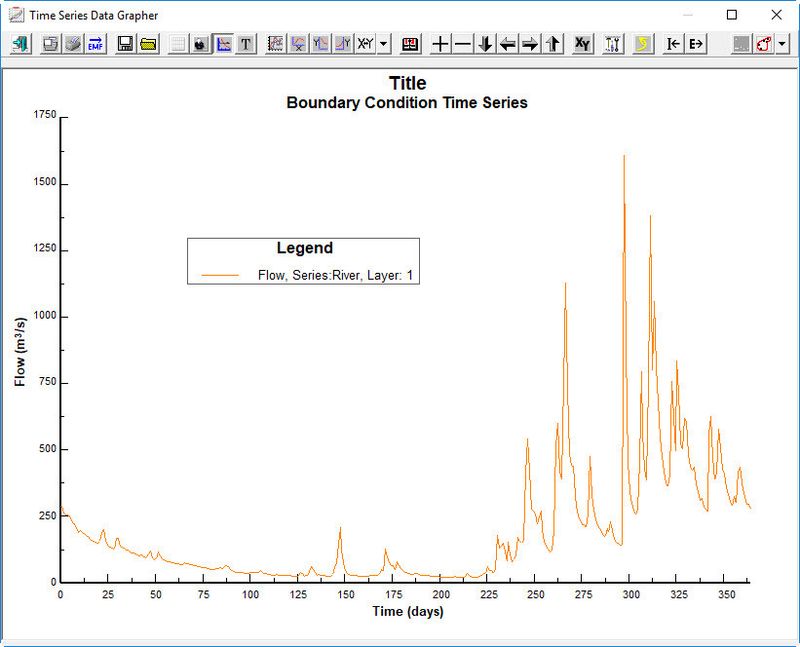
Figure 12 Flow time series plot.
4.2 Preparing the Tidal Level Boundary.
- Click to the E button
 which is next to Water Level (See 2381073 Figure 13)
which is next to Water Level (See 2381073 Figure 13) - Enter the Number of Series, which is 1 for this case (see 2381073)
- Enter the Title of Series as "Tides"
- Open "BC_Water Level.dat" file in Data folder, the copy and paste into the Data Series: Water surface form.
- Click Current button in the form to see the timeseries plot (see 2381073). Close timeseries data plot.
- Click OK to finish.
Another option for setting the open boundary is the Harmonic Boundary Series (Harmonic Boundary Series)
Figure 12 13 Assigning tidal boundary conditions.
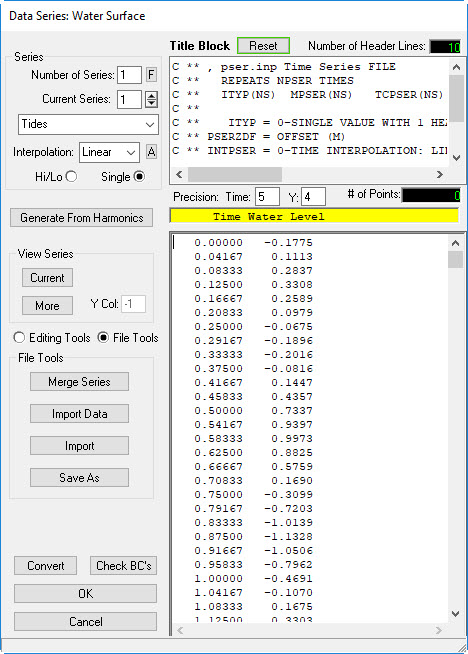
Figure 13 14 Preparing the tidal boundary series.
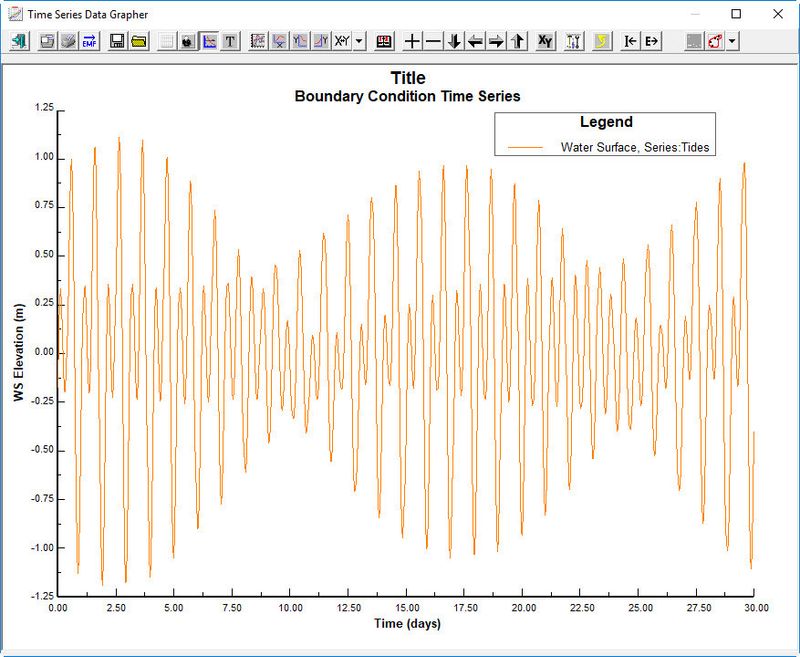
Figure 14 15 Tides time series plot.
4.3 Assigning Time Series to the Boundary Location Cells.
When all required boundary time series are prepared the next step is to assign those boundary time series to the model cells. Figure 14 shows the location of inflow and tidal level for the TraKhuc case.
4.3.1 Assigning the Flow Boundary In order to assign the flow boundary, the following steps should be taken
- Click to the ViewPlan icon
 on the main form (See Figure 15).
on the main form (See Figure 15). - Choose Boundary C’s in the Viewing Opt’s
 .
. - Check Enable Edit and Show Grid (See Figure 16).
- RMC on the inflow location cell/ choose New (See Figure 17).
- Enter the boundary group ID: River (See Figure 17).
- Select boundary types. It is dependent on your current boundary type to choose the suitable boundary type. In this case, we have a flow boundary so we choose number 1 (See Figure 17).
- Select the associated times series for this inflow boundary, "Flow" (See Figure 18).
- Click OK to complete.
- The boundary cells might have multiple cells to present the real river width. In order to assign the multiple cells, click Add by Polyline button in the form of Figure 18, you need to browse to the "US_BC Line.p2d" in the Data folder as shown in Figure 19 then click Apply button.
- Click All button to assign river flows to all cells ( See Figure 20)
- The inflow is now divided to the number of assigned cells. (See Figure 21).
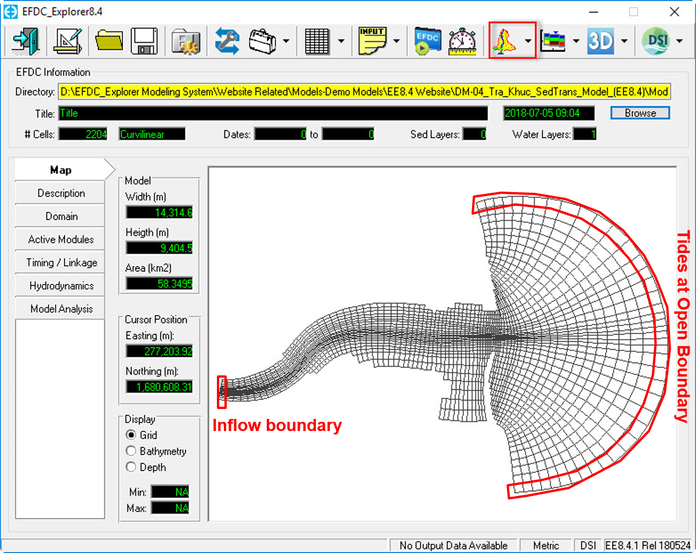
Figure 15 16 Locations of inflow and open tidal boundaries.
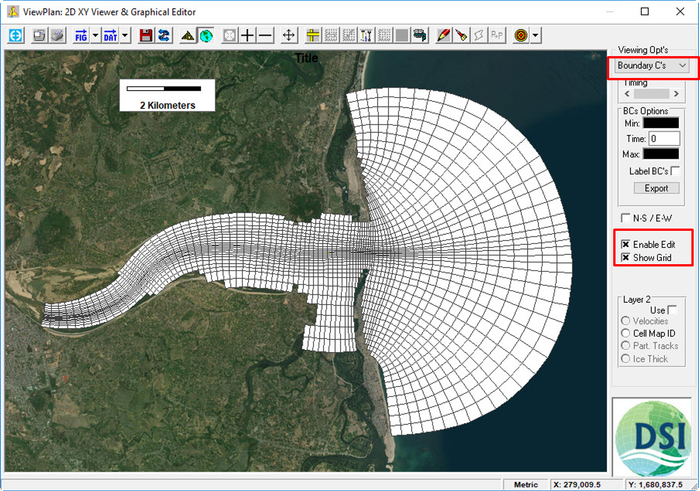
Figure 16 17 Assigning boundary condition cells.
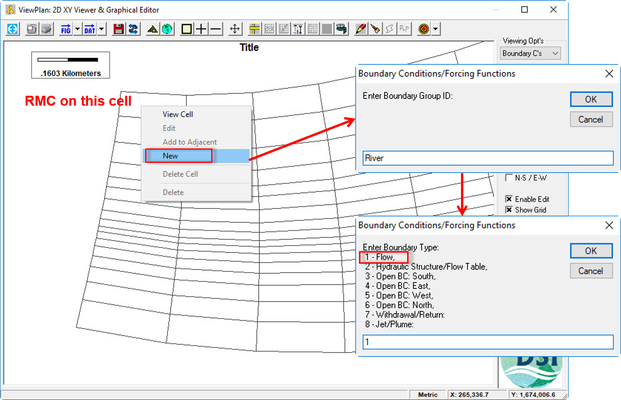
Figure 17 18 Create new boundary condition with RMC on the inflow cell.
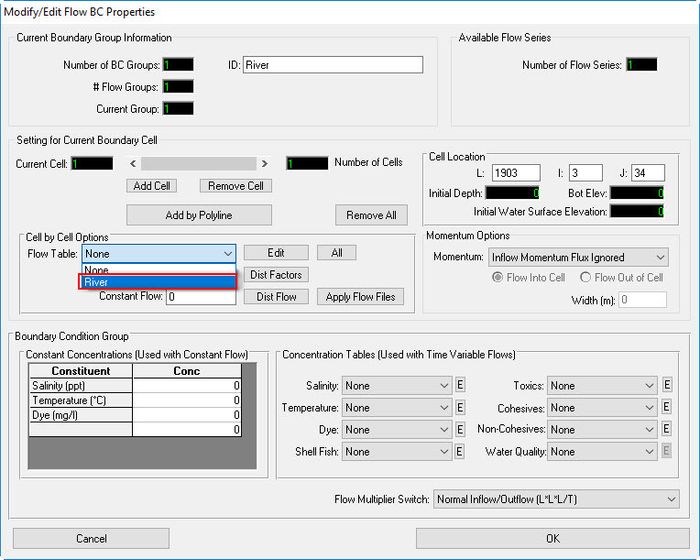
Figure 18 19 Assign the corresponding time series.
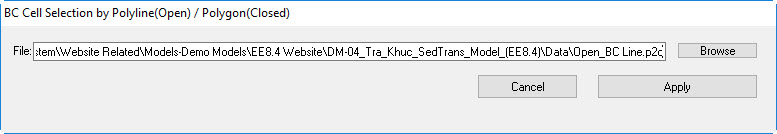
Figure 19 20 Assigning boundary cells by a polyline.
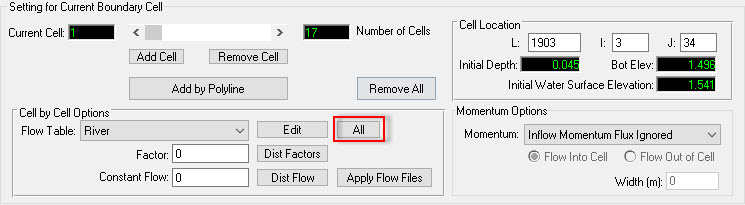
Figure 20 21 Assigning BC to all selected cells.
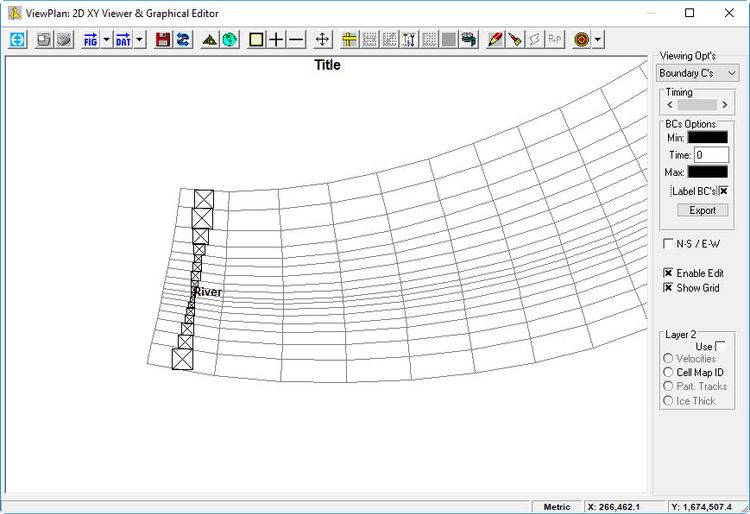
Figure 21 22 Upstream BC cells assigned.
...




























