Table of Contents
1 Introduction
This tutorial document will guide you how to setup a coastal hydrodynamic model by using the EFDC_Explorer (EE). It will cover preparation of the necessary input files for the EFDC model and visualization of the output by using the EFDC_Explorer (EE) Software.
The data used for this tutorial are from Tra Khuc Estuary in Vietnam. All files for this tutorial are found in Data folder downloadable from the EEMS website.
Before going to each session, let us first introduce the EE main form in order to better understand our explanation hereafter. Figure 1 is the main form of EFDC_Explorer or EE User Interface. The functions of individual icons are described in Knowledge Base.
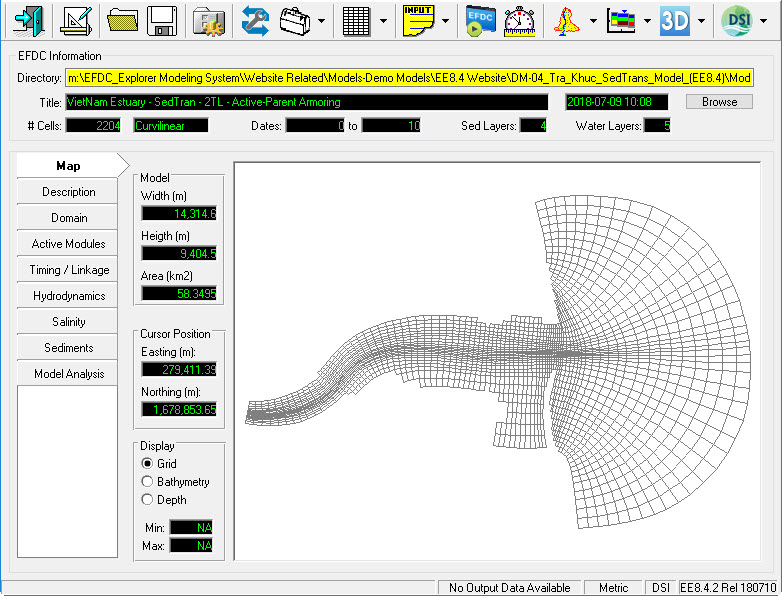
Figure 1 EFDC Explorer main form.
...
4 Assigning the Boundary Conditions
This section will guide you how to prepare for the boundary conditions and assign it to the model cell configuration. In this coastal case there are two flow boundaries; one is river discharge from the upstream and the other is tidal level. Thus, we should prepare two time series of inflow and tidal level boundaries for this particular case. In order to set a boundary time series the steps outlined below should be taken.
4.1 Preparing the Flow Boundary.
- Select the Domain/Boundary Conditions. (See Figure 9).
- Click to the E button
 which is next to Flow to edit the flow boundary. (Figure 9)
which is next to Flow to edit the flow boundary. (Figure 9) - Enter the Number of Series into the box which in this case is 1.
- Give a Title for associated time series, in this case "River".
- Click Import Data button, browse to "BC_Flow.dat" file in Data folder
- Select EE DAT or WQ Data format then click OK button. (See Figure 10).
- Enter "-1" in Import Data form then click OK button. (See Figure 11).
Click to the Current button  to view the current time series. If there are a number of layers then check Sum Layers to show total flow. (See Figure 12). Close timeseries data plot
to view the current time series. If there are a number of layers then check Sum Layers to show total flow. (See Figure 12). Close timeseries data plot
Click OK button in Data Series: Flow form to finish editing the boundary time series.
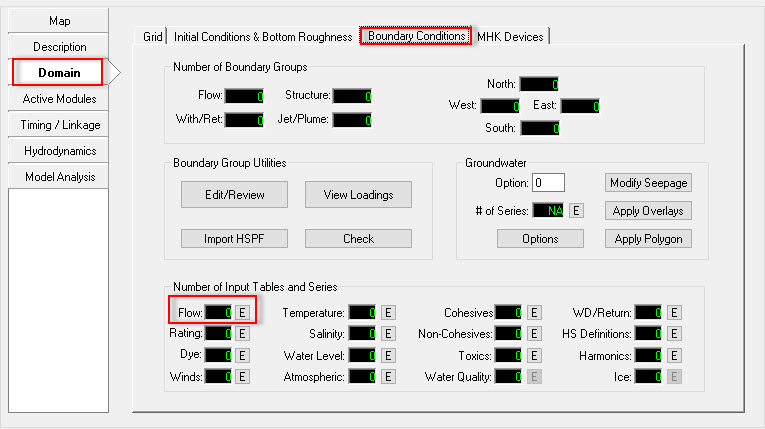
Figure 9 Assigning flow boundary conditions.
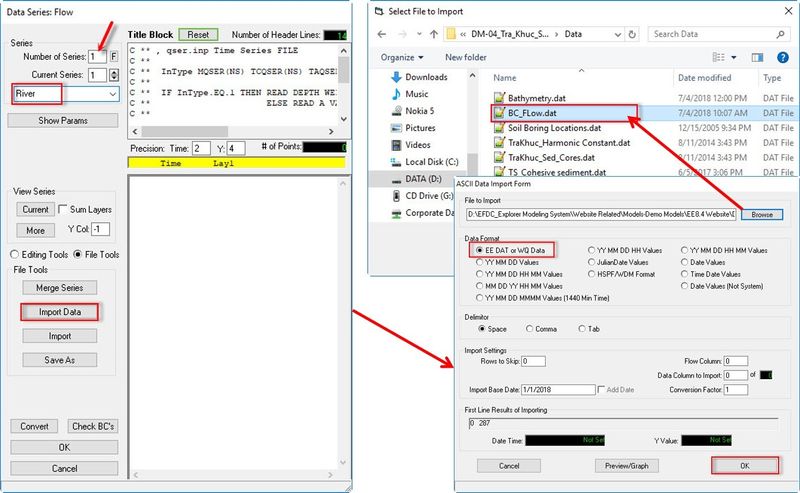
Figure 10 Editing the boundary time series (01).
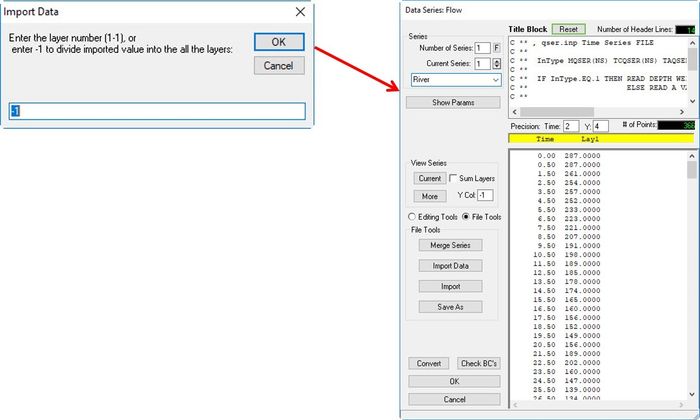
Figure 11 Editing the boundary time series (02).
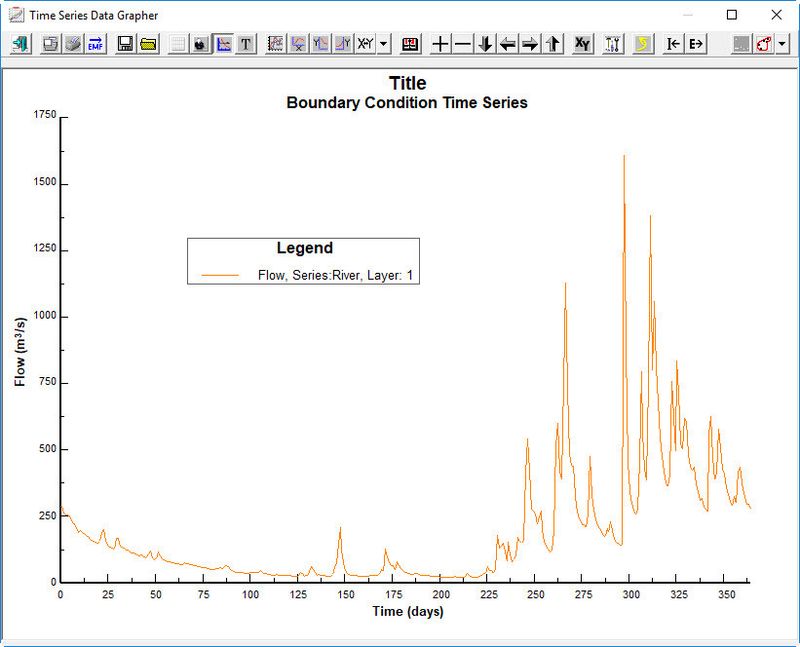
Figure 12 Flow time series plot.
4.2 Preparing the Tidal Level Boundary.
- Click to the E button
 which is next to Water Level (See Figure 13)
which is next to Water Level (See Figure 13) - Enter the Number of Series, which is 1 for this case (see 2381073 Figure 14)
- Enter the Title of Series as "Tides"
- Open "BC_Water Level.dat" file in Data folder, the copy and paste into the Data Series: Water surface form.
- Click Current button in the form to see the timeseries plot (see 2381073 Figure 15). Close timeseries data plot.
- Click OK to finish.
Another option for setting the open boundary is the Harmonic Boundary Series (Harmonic Boundary Series)
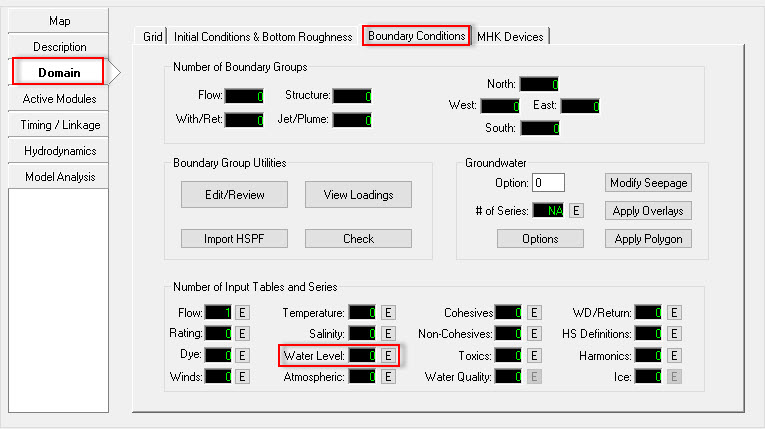
Figure 13 Assigning tidal boundary conditions.
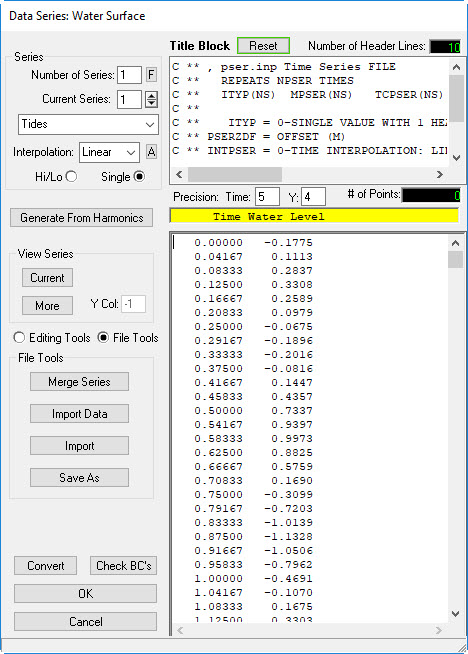
Figure 14 Preparing the tidal boundary series.
...
4.3 Assigning Time Series to the Boundary Location Cells.
When all required boundary time series are prepared the next step is to assign those boundary time series to the model cells. Figure 14 shows the location of inflow and tidal level for the TraKhuc case.
4.3.1 Assigning the Flow Boundary In order to assign the flow boundary, the following steps should be taken
- Click to the ViewPlan icon
 on the main form (See Figure 1516).
on the main form (See Figure 1516). - Choose Boundary C’s in the Viewing Opt’s
 .
. - Check Enable Edit and Show Grid (See Figure 1617).
- RMC on the inflow location cell/ choose New (See Figure 1718).
- Enter the boundary group ID: River (See Figure 1718).
- Select boundary types. It is dependent on your current boundary type to choose the suitable boundary type. In this case, we have a flow boundary so we choose number 1 (See Figure 1718).
- Select the associated times series for this inflow boundary, "Flow" (See Figure 1819).
- Click OK to complete.
- The boundary cells might have multiple cells to present the real river width. In order to assign the multiple cells, click Add by Polyline button in the form of Figure 1819, you need to browse to the "US_BC Line.p2d" in the Data folder as shown in in Figure 1920 then click Apply button.
- Click All button to assign river flows to all cells ( See Figure 2021)
- The inflow is now divided to the number of assigned cells. (See Figure 2122).
Figure 16 Locations of inflow and open tidal boundaries.
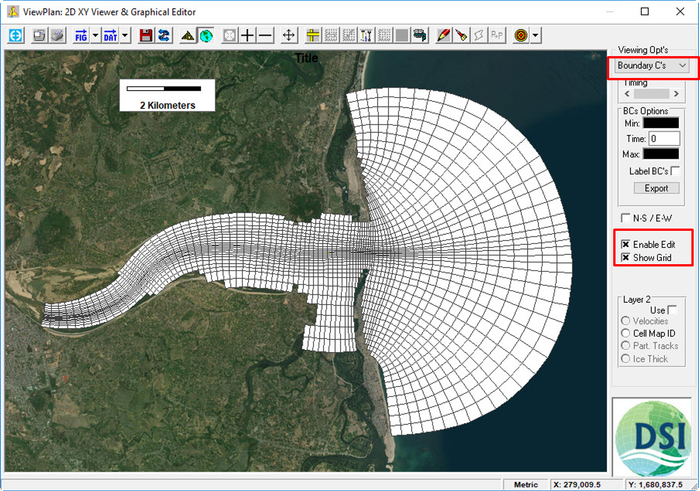
Figure 17 Assigning boundary condition cells.
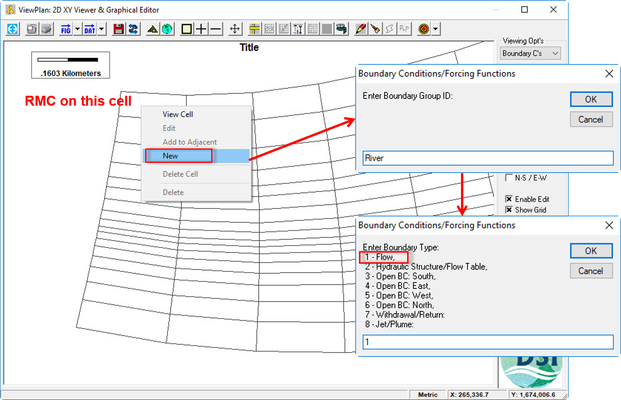
Figure 18 Create new boundary condition with RMC on the inflow cell.
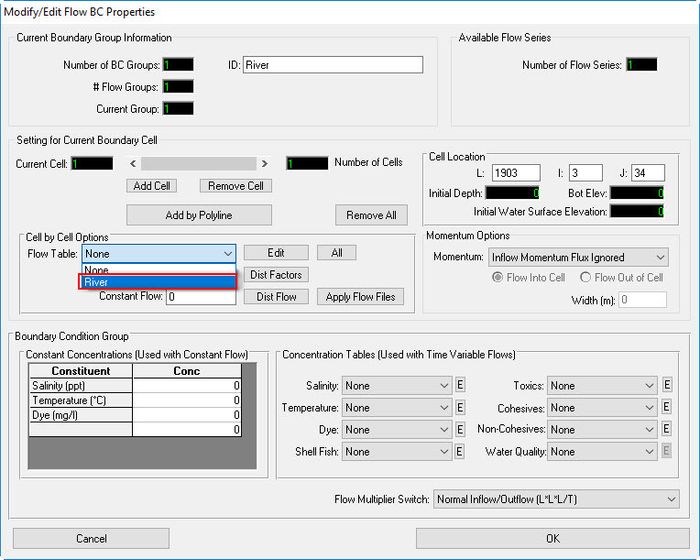
Figure 19 Assign the corresponding time series.
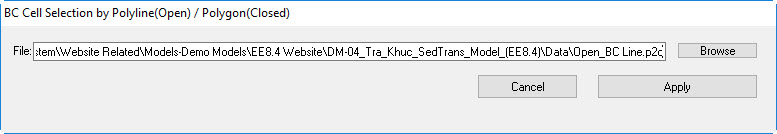
Figure 20 Assigning boundary cells by a polyline.
...
Figure 22 Upstream BC cells assigned.
4.3.2 Assigning Tides BoundaryIn order to assign the tides boundary, the following steps should be taken:
- Click to the ViewPlan icon
 on the main form (See Figure 1516).
on the main form (See Figure 1516). - Choose Boundary C’s in the Viewing Opt’s
 .
. - Enable editing the grid by checking Enable Edit
 (See Figure 1617)
(See Figure 1617) - RMC on the tidal location cell and select New (See Figure 2223)
- Enter the Boundary Group ID, "Ocean" (See Figure 2223)
- Select the appropriate boundary type. In this case, the river flows to the east, so choose "4" for the "Open BC:East" as shown in Figure 2223.
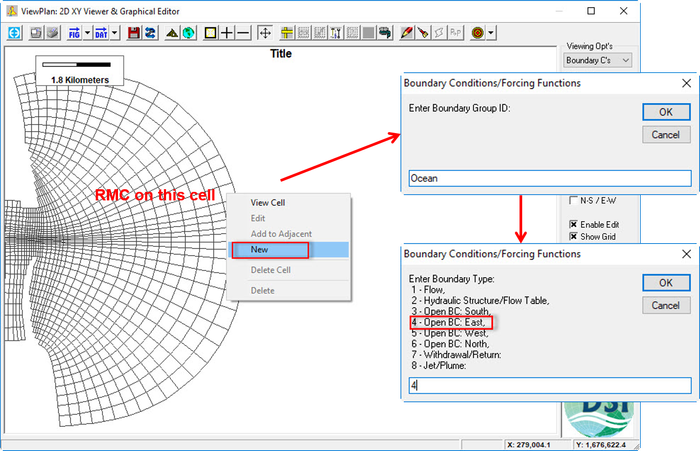
Figure 22 23 Set the tidal boundary.| Anchor |
|---|
Figure 23 | Figure 23
7. Select the water level time series that created earlier, "Tides" as shown in Figure 2524.

Figure 25 24 Assign tides boundary.
9. The open boundary often contains a lot of cells so it is not convenient to use the feature of Add to Adjacent cells that was used when we assigned the inflow boundary. In order to select multiple cells, we can to draw a line across all the cells as open boundaries. Then, click to Add by Polygon button (Figure 2524).
10. Browse to "Open_BC Line.p2d" in Data folder then click Apply and then OK button. (See Figure 2625).
11. Click Set All button in Figure 2524 to assign tides to all cells.
12. The tides is now assigned to all open BC cells. (See Figure 2726).
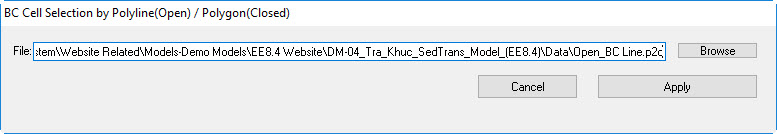
Figure 26 25 Selecting multiple BC cells by polyline/polygon.
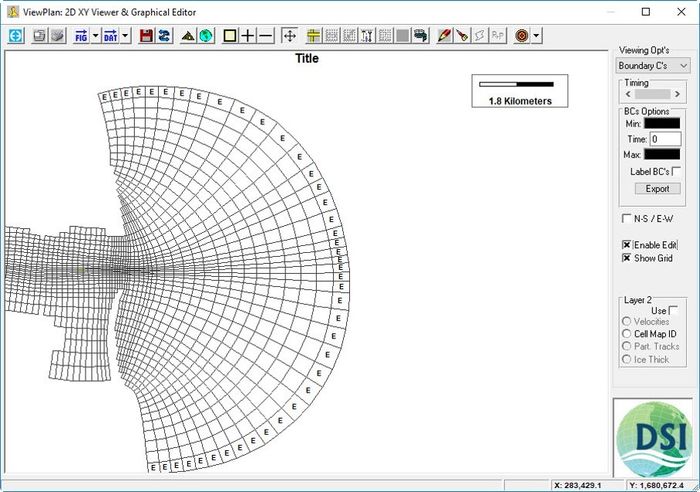
Figure 27 26 Tidal BC cells assigned.
5 Hydrodynamics Settings
In order to optimize simulation time, the EFDC model can be set so that dry cells are ignored with Wetting and Drying frame. In this case we should set this condition as following:
- Select Hydrodynamics/ Wetting & Drying box
- Set Flag is equal to -99.
- Entering the Wet/Dry Depth. Remember that the wet depth should always greater than the dry depth. (Figure 2827).
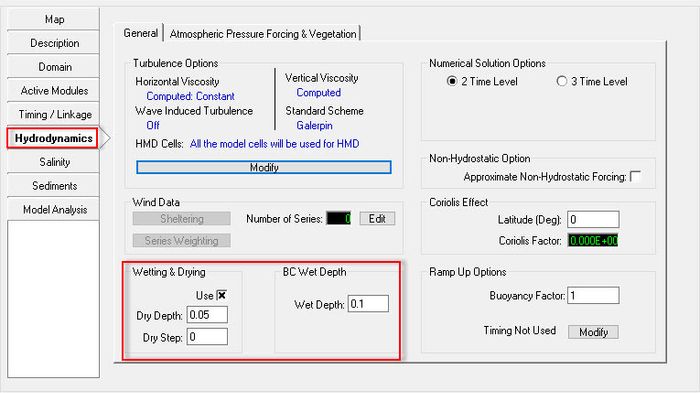
Figure 28 27 Hydrodynamic Model Setup.
4. Click Modify button in Turbulence Options to set turbulence diffusion ( See Figure 2928)
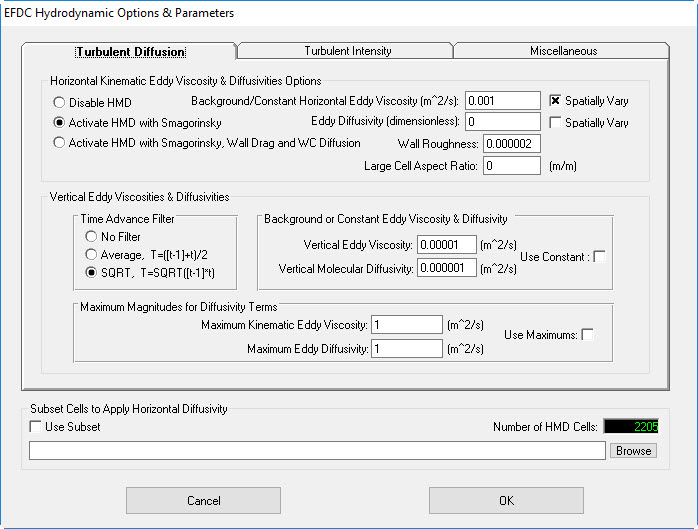
Figure 29 28 Turbulence Diffusion Settings.
...
6 Setting Vertical Layers
The hydrodynamic model is ready for running test now. Normally a model is run for one vertical layer for initial calibration and more vertical layers are added later. To increase the number of vertical layers:
- Open the Domain/ Grid tab and enter the number of vertical layers into the box as in this case the vertical layers are equal to 5 layers. (Figure 3029).
- Save the model project.
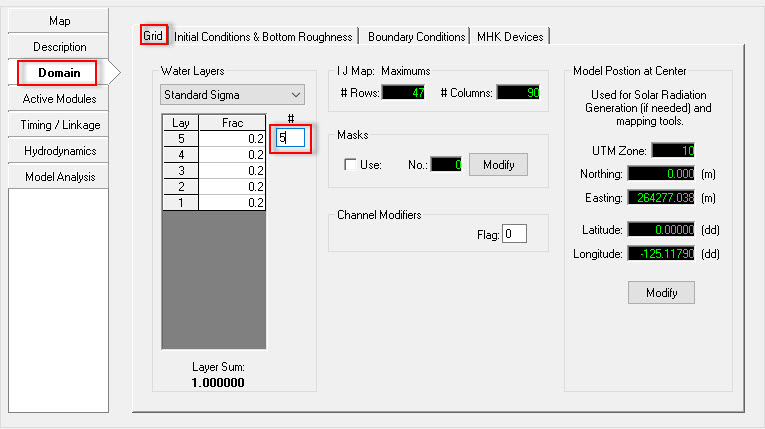
Figure 30 29 Setting the Vertical Layers.
7 Model Timing
We have now almost completed the hydrodynamic model. The final step is to set the model simulation time and model time steps.
- Select Timing/ Linkage and Model Run Timing (Figure 2827)
- Enter duration of starting/ ending the simulation. Note that the boundaries time series should be always covered this simulation duration period. Otherwise the model will not run.
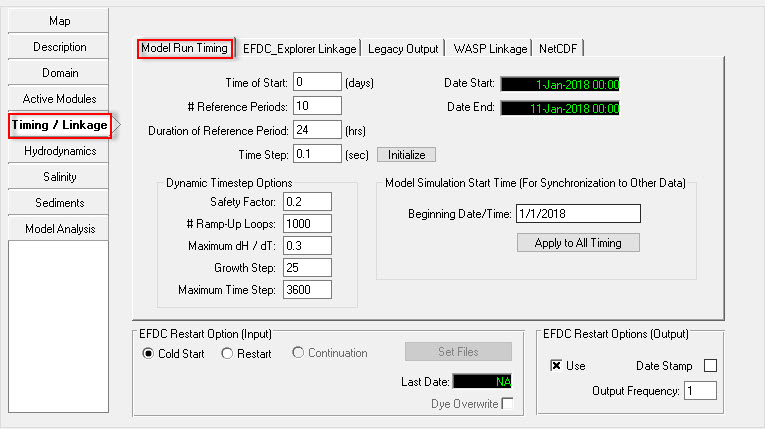
Figure 31 30 Setting the model run time.
3. Select the EFDC_Explorer Linkage tab to set the frequency of the output of the EFDC results. Setting this to 60 minutes means that EFDC will save the output every 15 minutes for display of the model results in the EE. (Figure 3231). Note that, smaller output frequency will create a larger output file.
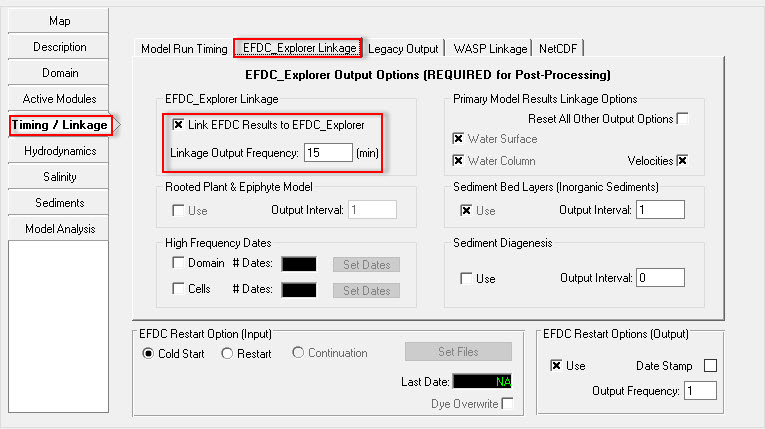
Figure 32 31 Setting Linkage Output Frequency.
8 Running EFDC+
- Select the Setting icon on the main form to browse to the EFDC+ executable file. (Figure 3332).
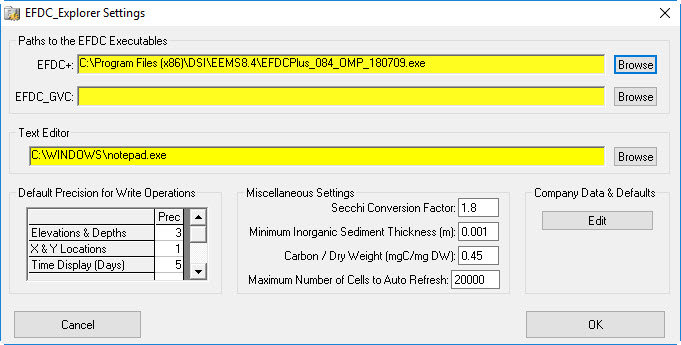
Figure 33 32 Browse to the EFDC executable file.
2. Select the Run EFDC icon to  on the main form and click the Run EFDC+ button to run the model (Figure 3433).
on the main form and click the Run EFDC+ button to run the model (Figure 3433).
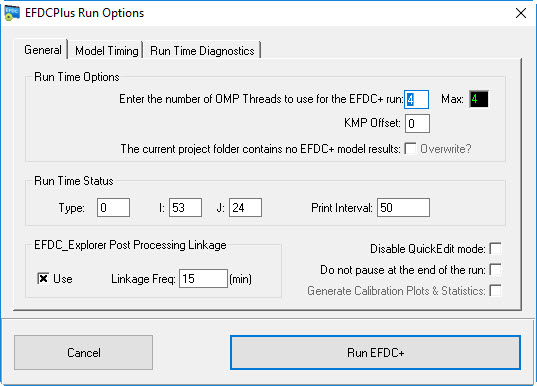
Figure 34 33 Run EFDC settings.
If you have correctly followed this example the model will start running and you will see the MS-DOS Window appear to shown the model results as see in Figure 3534. Note that you can hit any characters on the keyboard to pause the simulation and check the model results. If you want to exit the simulation hit the same key, if you want to continue run then hit any other key.
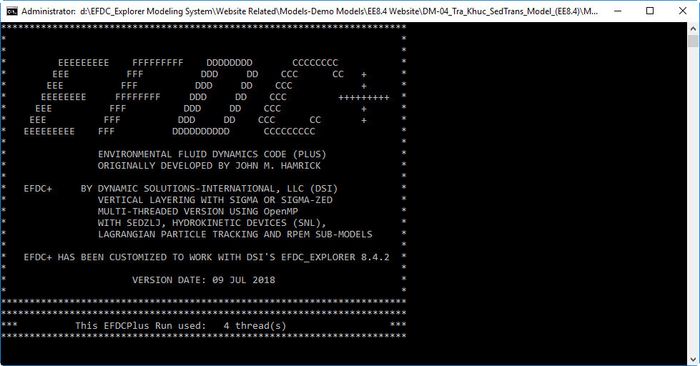
Figure 35 34 Running EFDC Window.
9 Visualizing the EFDC Solution
...
- Select the ViewPlan button.
- Scroll drown the Viewing Opt’s to choose the parameters that you want to view the model results. Figure 3635 is an example of showing the vector and magnitude velocity field results. Similarly, you can select other parameter to show the results.
- RMC on to the legend scale to access the ViewPlan Display Options (Figure 3736).
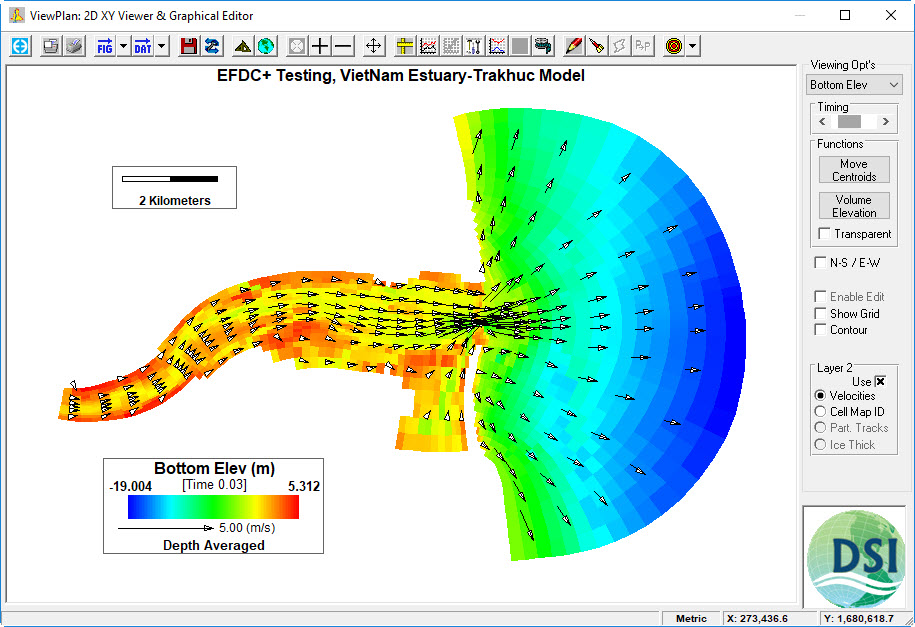
Figure 36 35 Visualizing the EFDC+ solution.
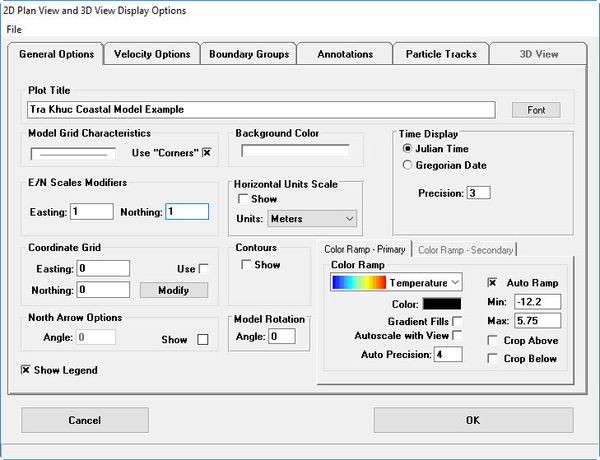
Figure 37 36 ViewPlan Display Options.
...
There are few main features in the Toolbar that are very often used when analyzing the model results. Explanations for these buttons provided in Table 1 below.
...


































