...
| Table of Contents | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1. Introduction
This tutorial document will provide a guideline on how to set up a coastal hydrodynamic model by using the EFDC+ Explorer (EEMS). It will cover the preparation of the necessary input files for the EFDC model and visualization of the output by using the EFDC+ Explorer Software.
The data used for this tutorial are from Tra_Khuc Estuary in Vietnam. All files for this tutorial are found in Data folder downloadable from the EEMS Website.
Before going to each session, let us first introduce the EE main form in order to better understand our explanation hereafter. Figure 1 is the main form of EFDC+ Explorer or EE User Interface. The functions of individual icons are described in Model Control Form.
Anchor Figure 1 Figure 1
Figure 1. EFDC+ Explorer main form.
2. Create a New Grid
This section will provide guidelines on how to create a new simple gird with EFDC+ Explorer. For a complicated grid, users are recommended to use specialized grid generation software such as Grid+.
Tra_Khuc Estuary in Quang Ngai province, Vietnam is chosen as the example of building a 3D coastal model.
The gird generation process includes the following steps:
1.Open EE
2.Click on icon New Model on the main menu of EE interface.
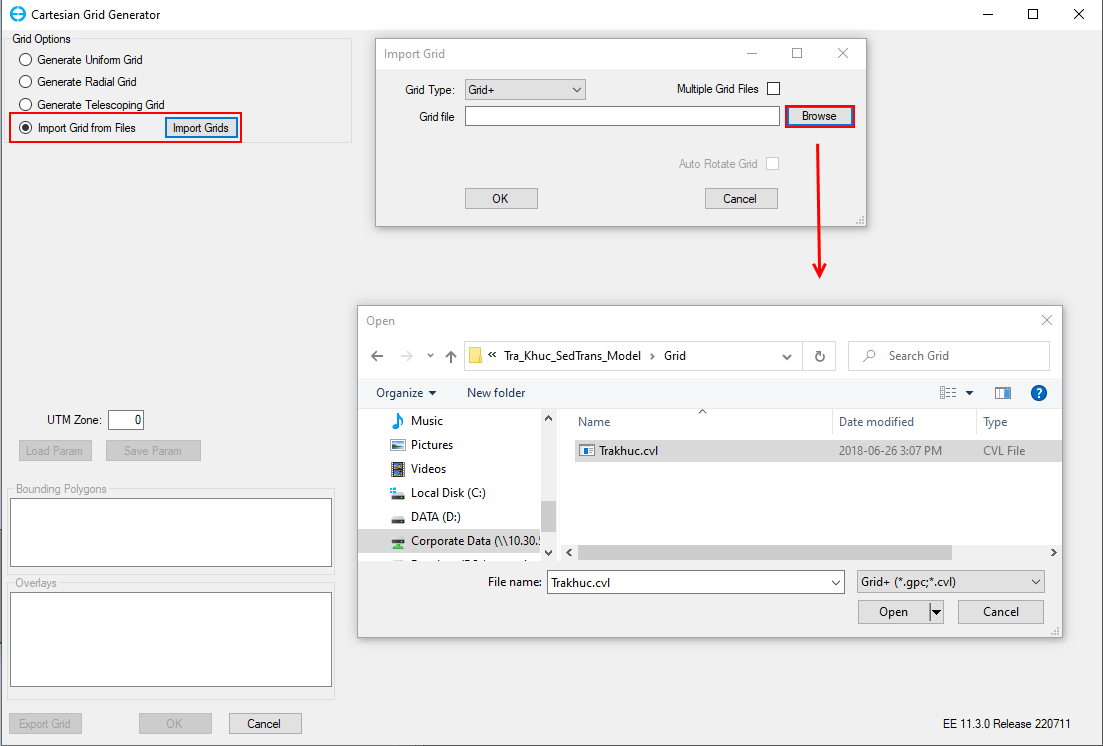
3. In Grid Tool, select Import Grid from Files and click Import Grids button. Users should choose Grid type as Grid+ and then click Browse button to select the grid file name as "Tra_Khuc.cvl" in Grid folder as shown in Figure 2. On the other hand, EE also supports users to import various formats of grid files with the option Grid type.
Anchor Figure 2 Figure 2
Figure 2. Import grid file.
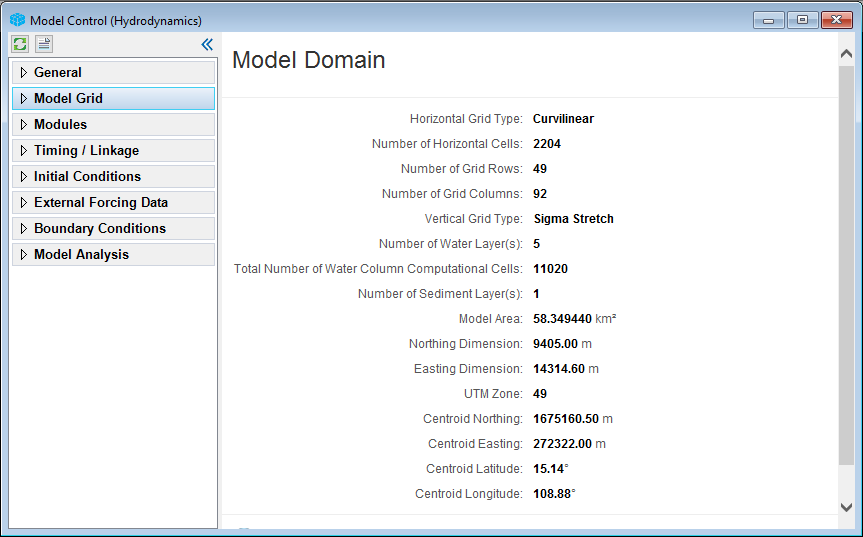
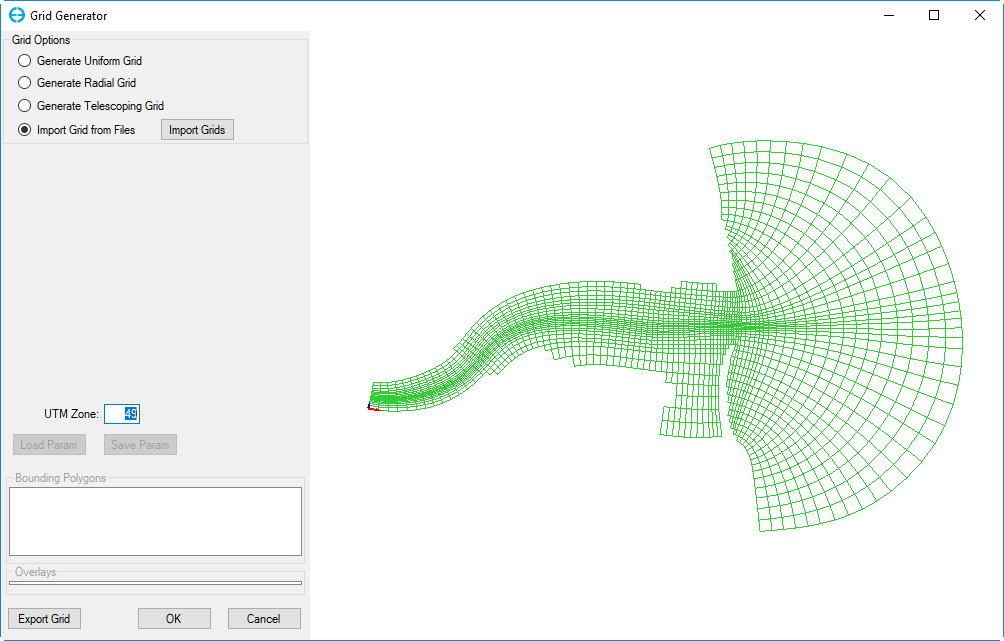
4. Set UTM Zone is 49 and then click OK to load the grid in Figure 3.
Anchor Figue 3 Figue 3
Figure 3. Load grid file.
5. Save the model by selecting this button in the main toolbar and create a new directory (as shown in Figure 4)
Anchor Figure 4 Figure 4
Figure 4 New model saved.
3. Assigning the Initial Conditions
This section will show how to assign the initial conditions such as the bathymetry, and water level.
Figure 5. Assigning initial conditions.
3.1 Assigning the Bathymetry
- Right mouse click (RMC) on Bathymetry in the Model Control tab. A popup Bathymetry tab will appear as presented in Figure 6, click Assign button.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
3.2 Assigning the Depth/Water Surface Elevations
The next steps show the way to assign the initial depth or water surface elevations.
- RMC on Water Depth/Elevation in Model Control tab. A popup Water Depth/Surface Elevation tab will appear as presented in Figure 11, click Assign Elevation button.
...
4. Assigning the Boundary Conditions
The main aim of this section is to show how to prepare for the boundary conditions and assign them to the model cell configuration. In this coastal case, there are two flow boundaries; one is river discharge from the upstream and the other is tidal level. Thus, users should prepare two time series of inflow and tidal level boundaries for this particular case. In order to set a boundary time series the steps outlined below should be taken.
4.1 Preparing the Flow Boundary.
...
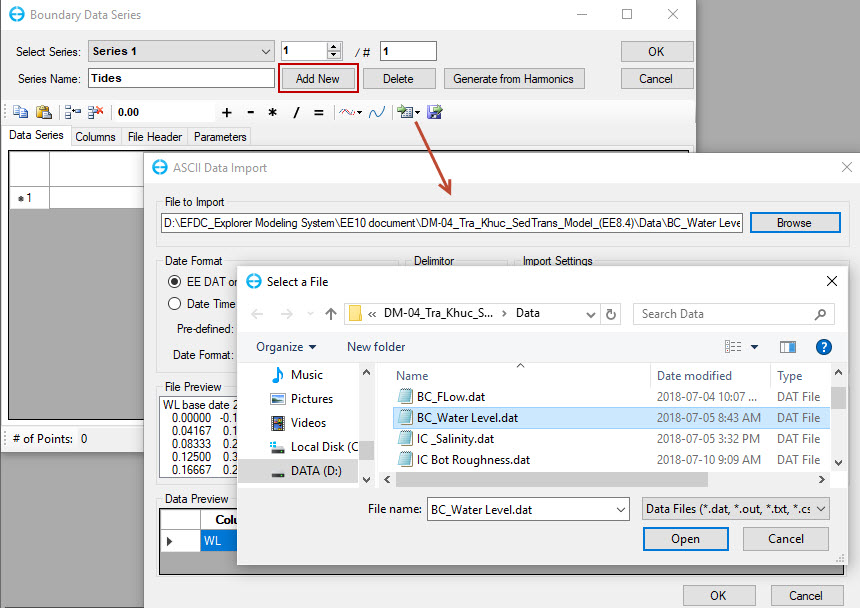
2. Click on Add New to insert a new data series and name it "Tides" in Series Name. Browse to the "BC_Water Level.dat" file in the Boundaries folder and click Open to import data file (shown Figure 22).
Anchor Figure 22 Figure 22
Figure 22. Import water level time series.
...
4.3 Assigning Time Series to the Boundary Location Cells.
When all required boundary time series are prepared the next step is to assign those boundary time series to the model cells.
4.3.1 Assigning the Flow Boundary
...
4.3.2 Assigning Tides Boundary
In order to assign the tides boundary, the following steps should be taken:
1.Click to the 2DH View icon on the main form.
2. In View Layer Control, turn on the Model Grid layer and turn on the editing model of the Boundaries Layer by clicking the pencil icon shown as Figure 25.
3. Clicking on Selection Tool in the main toolbar and then select Inside Polygon as Figure 31.
Anchor Figure 31 Figure 31
Figure 31. Select inside polygon.
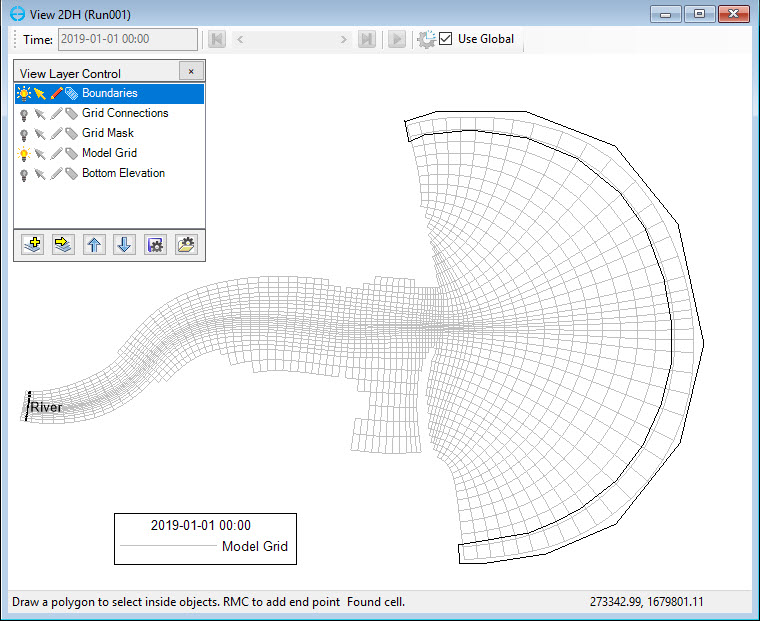
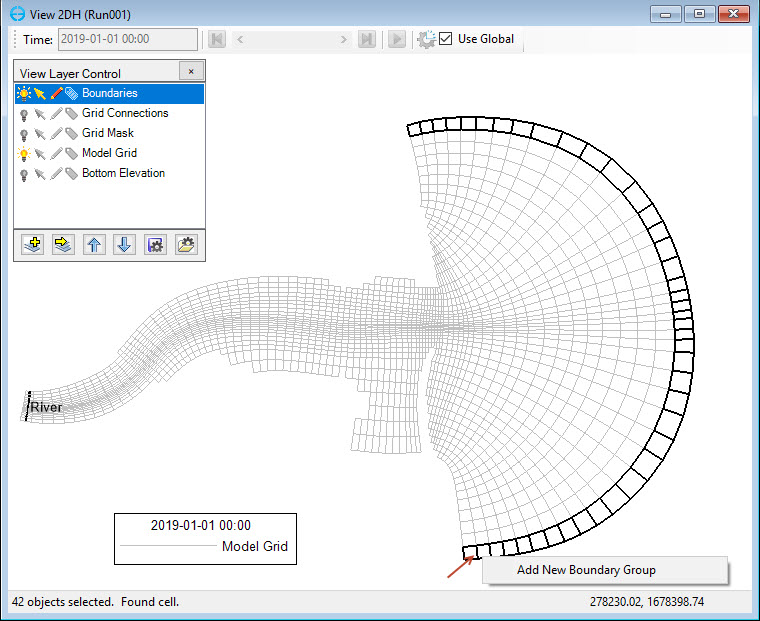
4. Draw a polygon that can cover all the cells at the tides boundary location in Figure 32.
Figure 32. Draw a polygon to assign tides boundary.
5. To assign the tides boundary group, users should RMC on a selected cell and click Add New Boundary Group as 225902604 Figure 33.
Anchor Figure 33 Figure 33
Figure 33. Add new tides boundary group.
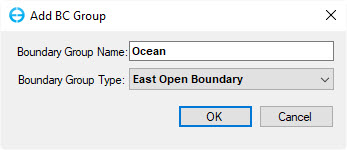
6. Enter the Boundary Group Name, "Ocean" and select the appropriate boundary type as 225902604 Figure 34. In this case, the river flows to the east, so choose " East Open Boundary".
Anchor Figure 34 Figure 34
Figure 34. Set up tides boundary.
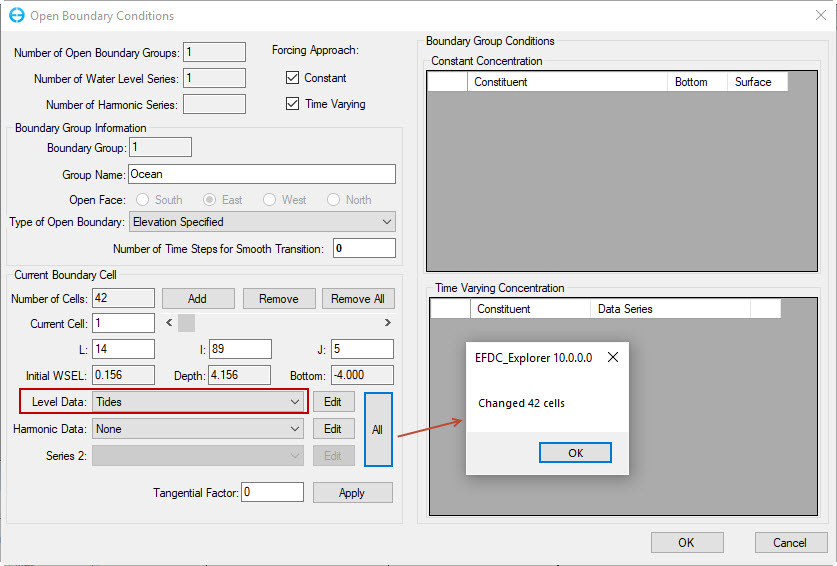
7. Select level data time series that were created earlier, "Tides" as shown in Figure 35. Next, click All button to assign tides to all cells. The number of changed cells will be informed and click OK.
Anchor Figure 35 Figure 35
Figure 35. Assign tide flow boundary.
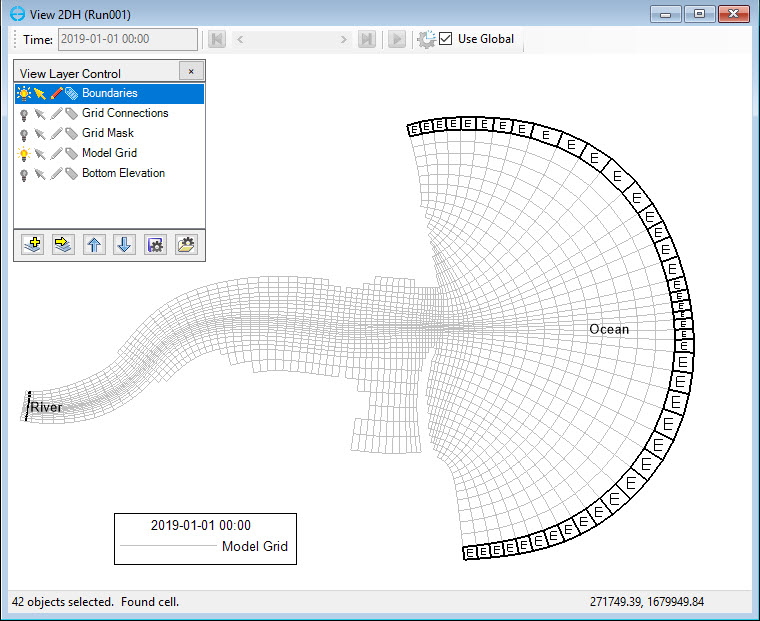
8. The tides open boundary is now assigned for all selected cells as presented in 225902604 Figure 36.
Anchor Figure 36 Figure 36
Figure 36. Tides boundary cells are assigned.
5. Hydrodynamics Model
- Back to the main tab, select Windows in the toolbar and click to Model Control, or select Model | Show Active Model from the main menu.
Figure 37. Use the Windows option to return to the Model control tab.
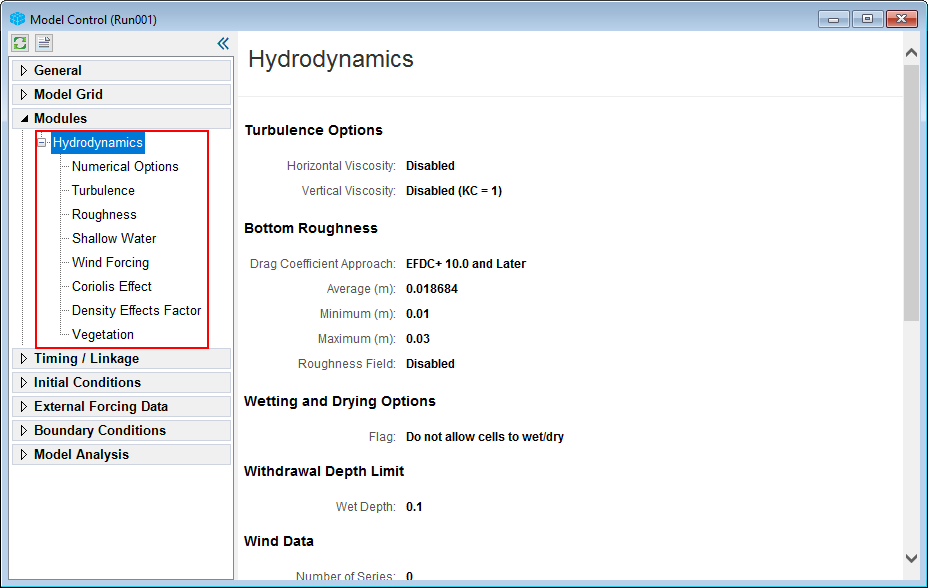
2. In Modules sub-main tab, click + to expand Hydrodynamics tab, all sub-tabs of Hydrodynamics will be shown as Figure 38. The users need to RMC on each sub-tab to adjust option settings.
Anchor Figure 38 Figure 38
.
Figure 38. Hydrodynamic options setup.
3. Set Roughness
RMC on Roughness. A popup Bottom Roughness tab will appear as presented Figure 39, click Assign button.
...
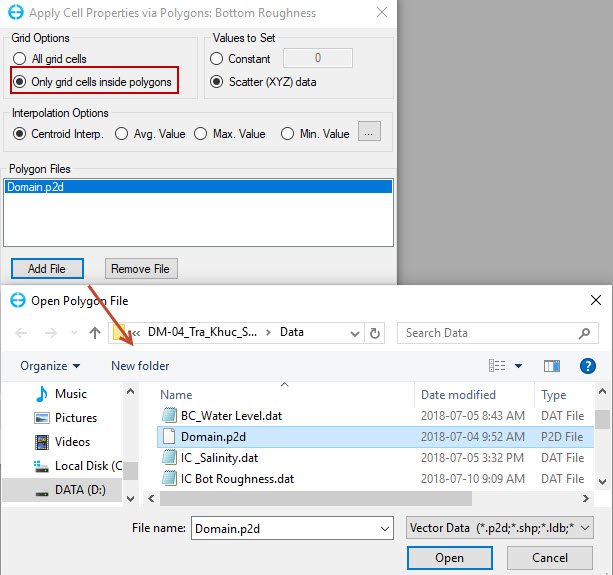
For Grid Options, select option Only grid cells inside polygons. In Polygon Files, users should click Add File button to browse the file "Domain.p2d" in the Bathymetry folder . (Figure 40) .
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Figure 40. Load polygon file.
...
Figure 42. Results of assigning bottom roughness.
4. Setting Wetting and Drying
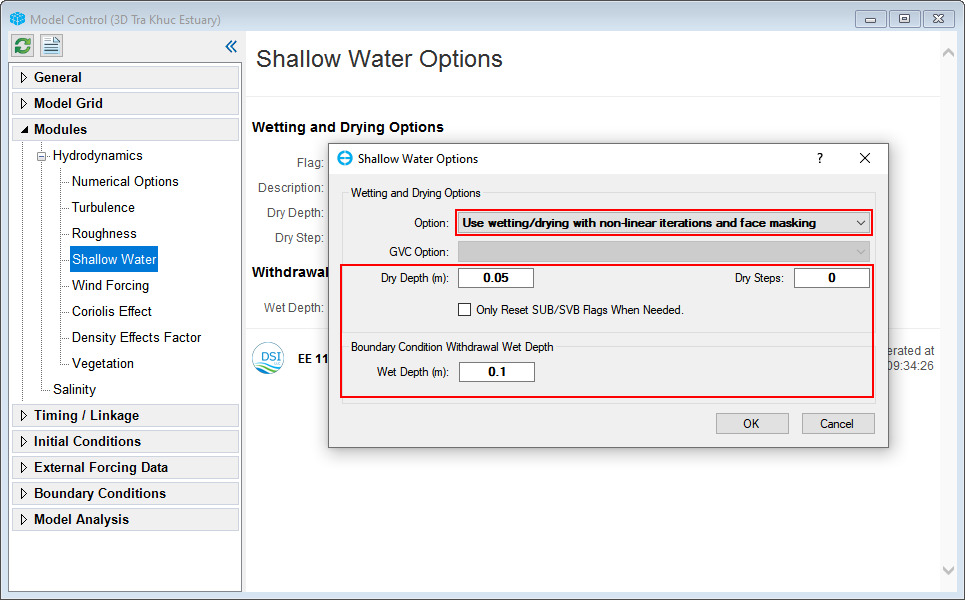
The Shallow Water settings are important in coastal simulations. In this case, users should set the Shallow Water Options as in Figure 43.
Anchor Figure 43 Figure 43
Figure 43. Wetting and Drying setting for the model.
5. Setting Turbulence
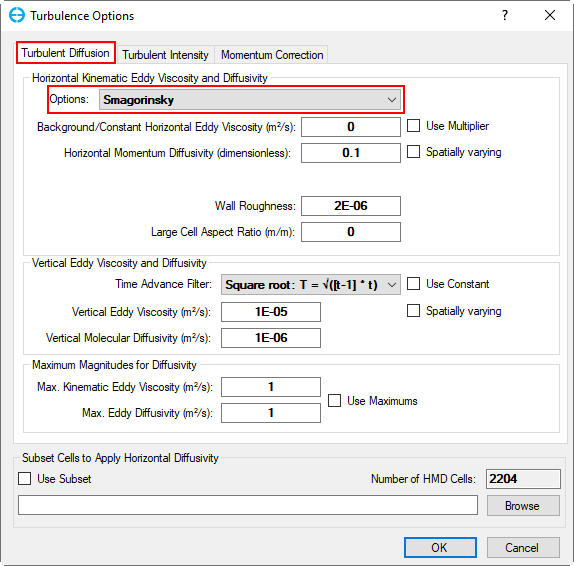
RMC on Turbulence sub-tab, in the Turbulence Options, select Turbulent Diffusion to set turbulence diffusion. Select options as "Smagorinsky" and click OK ( as 225902604as shown in Figure 44).
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Figure 44. Turbulence Diffusion Settings.
6. Salinity Model
6.1 Activate Salinity Modules
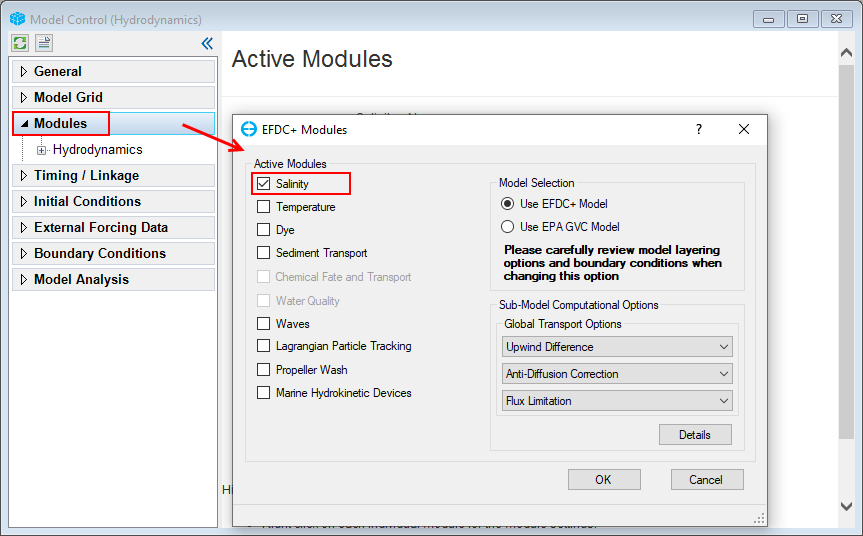
In the Model Control form, RMC on Modules to open the EFDC+ Modules window. In the EFDC+ Modules, check the Salinity checkboxes and then click OK (as shown in 225902604 Figure 45). The Salinity item will then be added under Modules.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Figure 45. Active EFDC+ modules form.
6.2 Salinity Module Setting
6.2.1 Salinity Initial Condition
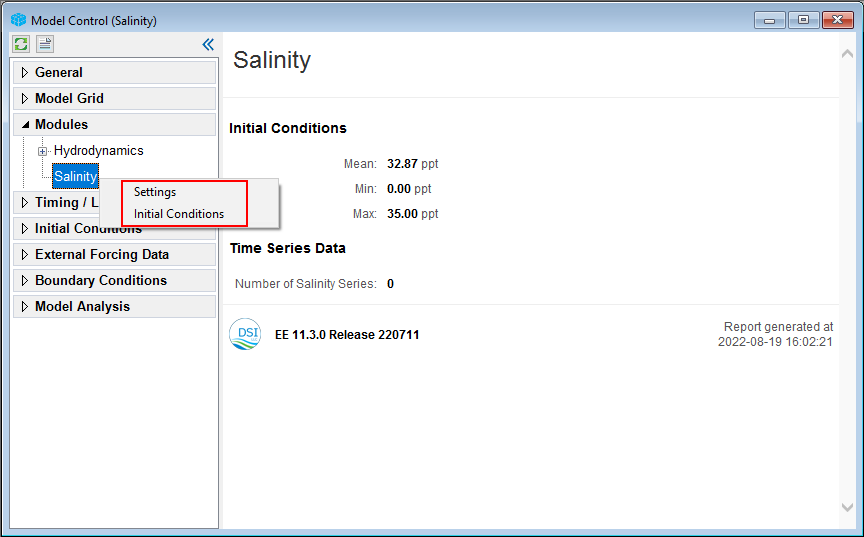
From the Model Control form, RMC on the Salinity module sub-tab under the Modules tab; a list of options will appear for the user to select, as shown in 225902604 Figure 46 below.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Figure 46. General salinity module setting options.
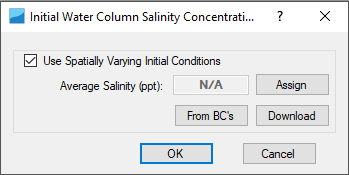
After clicking Initial Conditions, form of Initial Water Column Salinity Concentration will appear as shown in 225902604Figure 47.
Anchor Figure 47 Figure 47
Figure 47. Salinity initial conditions.
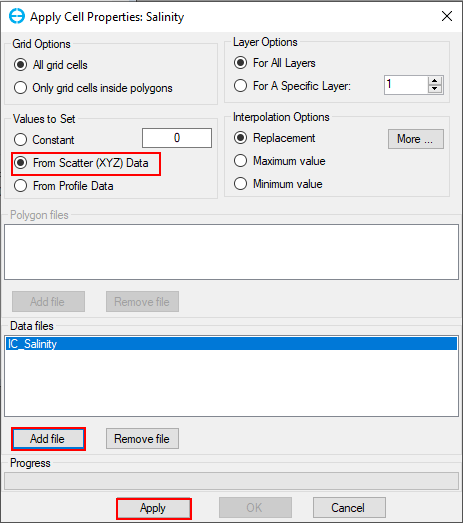
After clicking on Assign button, the Apply Cell Properties: Salinity form will appear. In this form, which is shown in 225902604 Figure 48 below user should follow these steps:
- In the Values to Set frame, select From Scatter (XYZ) data
- In the Data Files frame, click on the Add File button to browse to the salinity time series file name “IC_Salinity.dat”
- Click on Apply Defined Conditions to assign salinity initial condition. This sets the salinity data for the model.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Figure 48. Apply cell properties for salinity.
6.2.2 Assign Boundary Concentration
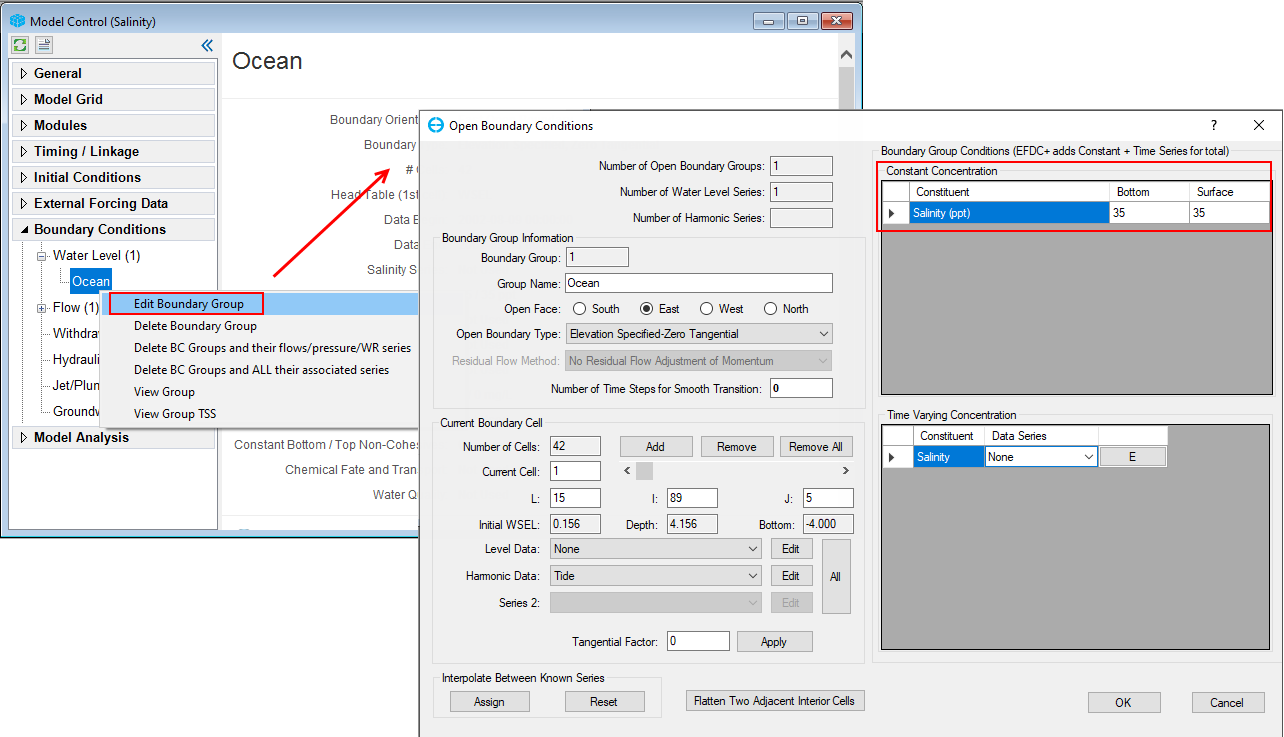
Returning to the Model Control form and do the following steps as shown in 225902604 Figure 49 to assign the salinity to boundary groups.
- Expand the Boundary Conditions tab on the left side of the screen; then expand the Water Level group; RMC on the Ocean group; then select Edit Boundary Group to open the Open Boundary Conditions
- In the Boundary Group Conditions frame of the Open Boundary Conditions form, under the Constant Concentration tab, set the salinity concentration of the bottom and surface layer as 35ppt
- Click the OK button to save the settings.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Figure 49. Set the constant salinity in the ocean boundary.
7.Setting Vertical Layers
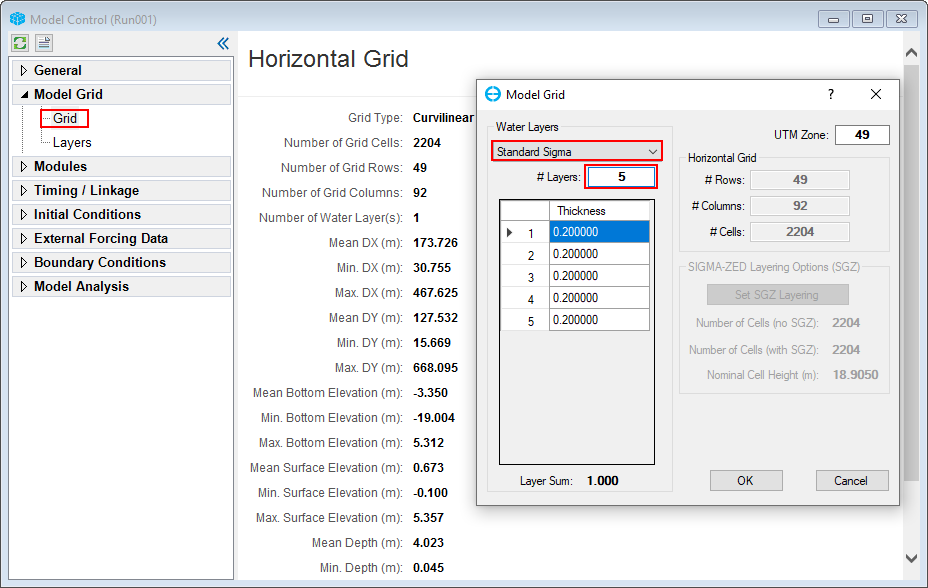
The model is ready for running a test now. Normally a model is run for one vertical layer for initial calibration. It is also possible to add more vertical layers by the following steps (as shown in 225902604 Figure 50):
- RMC on Grid in the Model Grid.
- Select Standard Sigma
- Enter the number of vertical layers into the box (# Layers). For Tra_Khuc case, set vertical layers to 5 layers and then click OK to save the setting.
Anchor Figure 50 Figure 50
Figure 50. Setting the vertical layers.
8. Model Timing
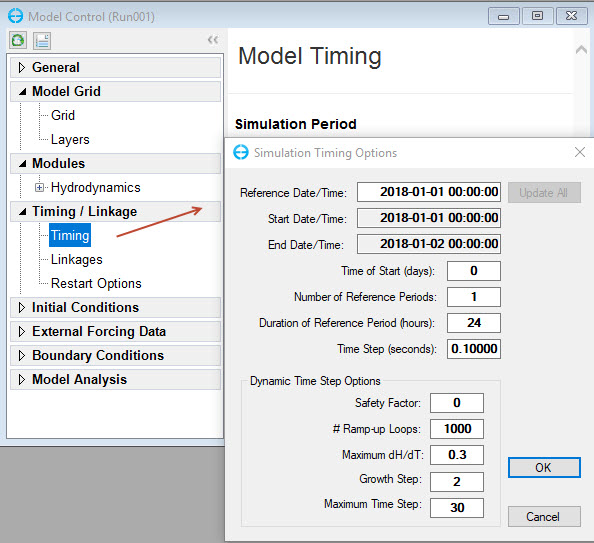
The final step is to set the model simulation time and model time steps.
- In the Timing / Linkage, RMC on Timing. Enter the duration of starting/ ending the simulation as 225902604 Figure 51. Note that the boundaries time series should be always covered in this simulation duration period. Otherwise, the model will not able to run.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Figure 51. Setting the model run time.
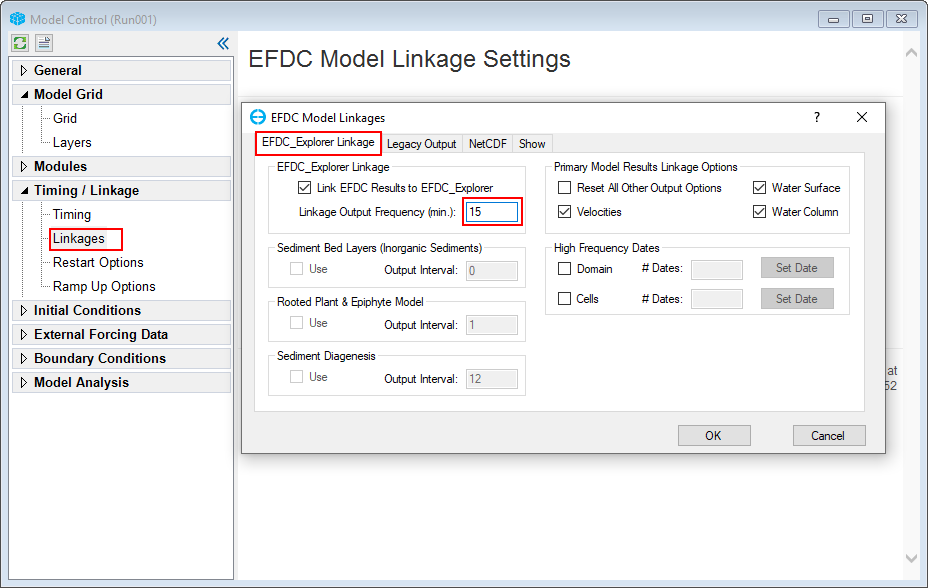
2. RMC to Linkages and select the EFDC+ Explorer Linkage tab to set the frequency of the output of the EFDC results. Setting this to 15 minutes means that EFDC will save the output every 15 minutes for the display of the model results in the EE . (225902604Figure 52). Click OK button
Note that, the smaller output frequency will create a larger output file.
Anchor Figure 52 Figure 52
Figure 52. Setting Linkage Output Frequency.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
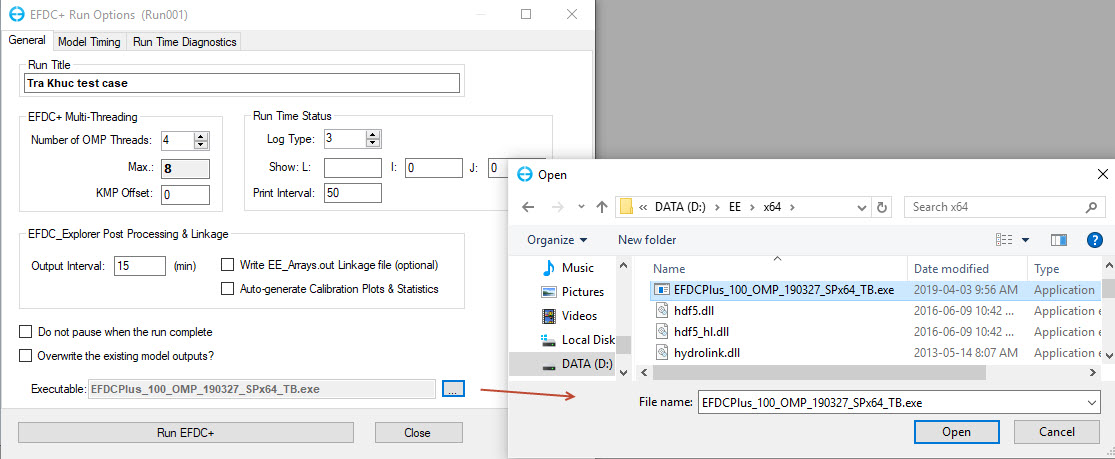
Figure 54. Running EFDC Window.
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Note that users can hit any characters on the keyboard to pause the simulation and check the model results. If they want to exit the simulation hit the same key if they want to continue running then hit any other key. |
10. Visualizing the Model Output
This session will show how to view the model simulation results.In general, users can access the main form to click 2DH View button to view the model simulation results.
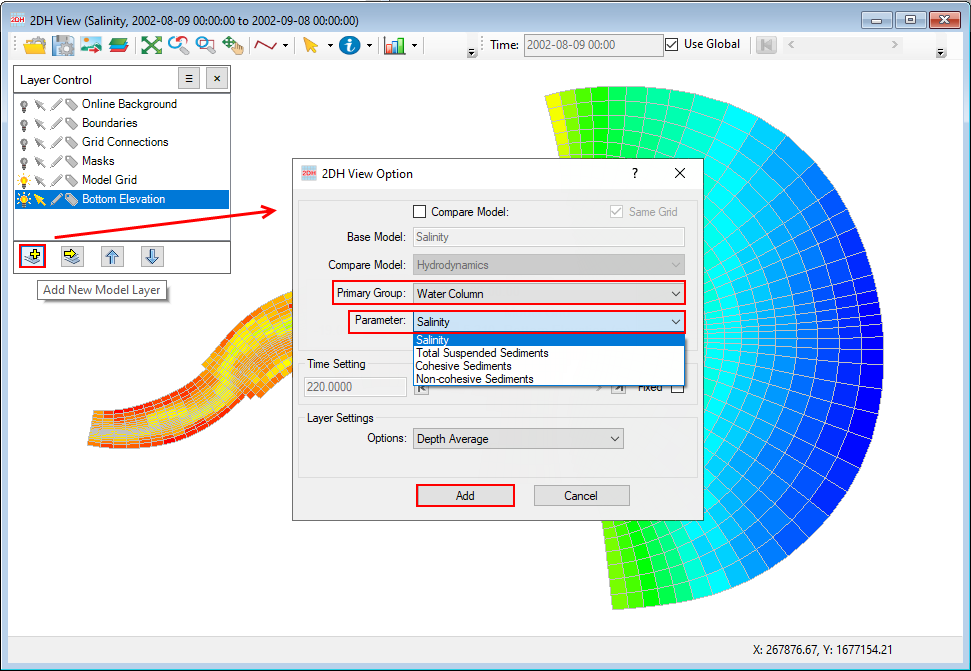
- InLayer Control,click Add button to add a New EFDC View Layer . The users should see the 2DH View Options window with Primary Group and Parameter to display (as 225902604shown in Figure 55), after selecting the parameter the users should click Add button to add the layer in 2DH View.
Anchor Figure 55 Figure 55
Figure 55. Parameter visualization.
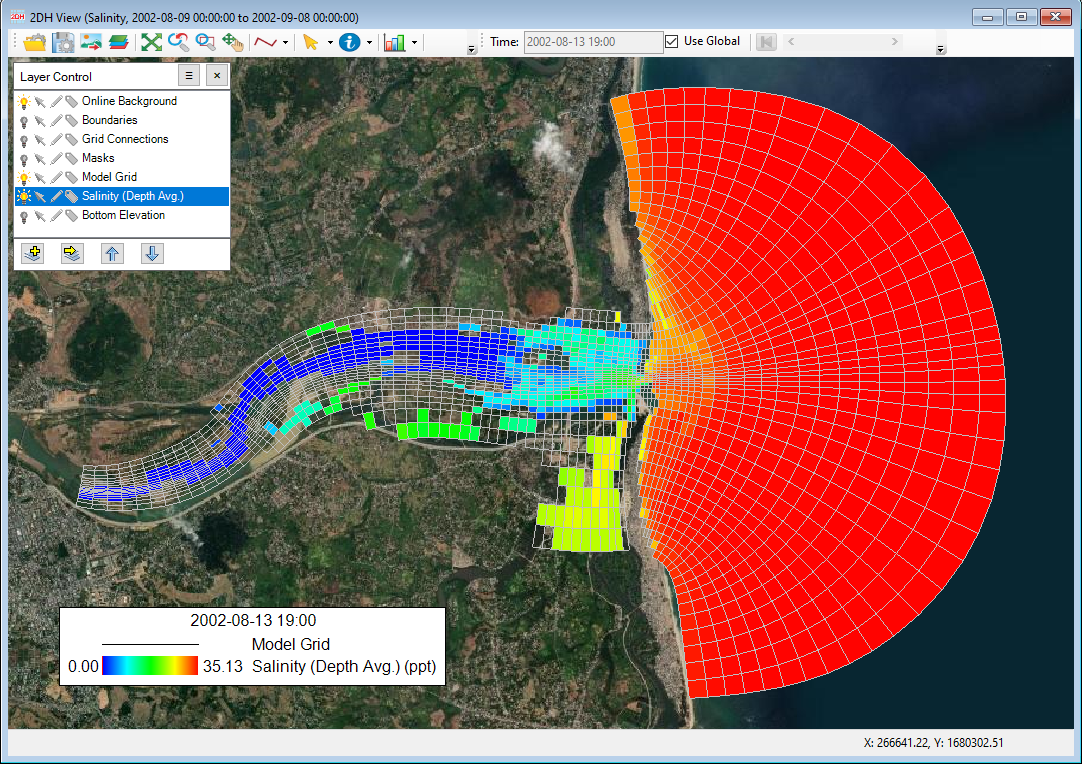
2. 225902604Figure 52 is an example of showing the salinity results. Similarly, EE is able to support the visualization of other model parameters.
Anchor Figure 52 Figure 52
Figure 56. Velocity vector visualization.
Please refer to the “EFDC+ Explorer User’s Manual” for more information on EE capabilities.