1 Introduction
...
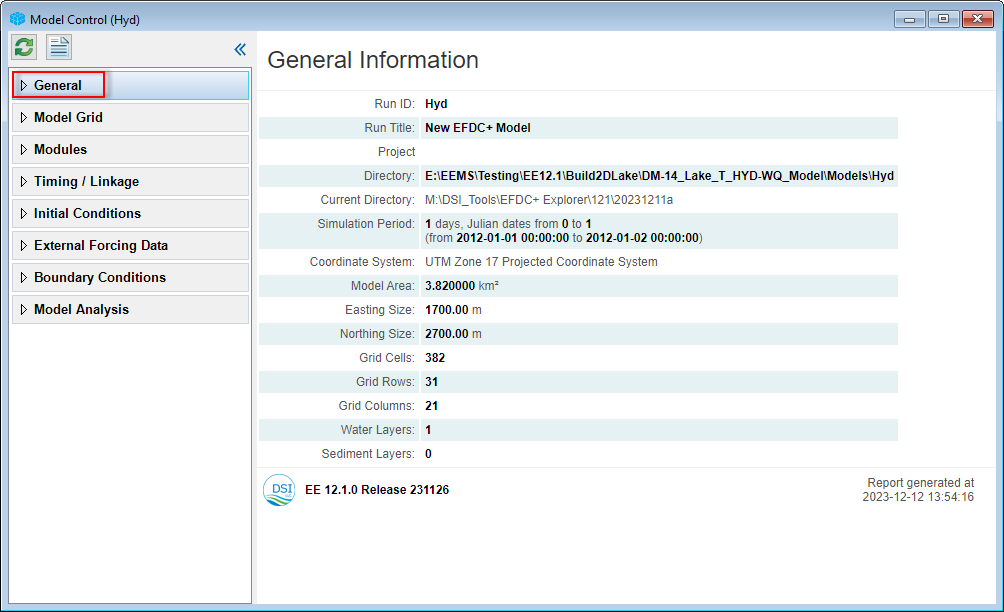
Before beginning the first session, let us first introduce the main form of the EE GUI in order to better understand our explanations in this document. Figure 1- 1 is the main form of EFDC+ Explorer or EE User Interface.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Figure 1- 1. EFDC+ Explorer main form.
...
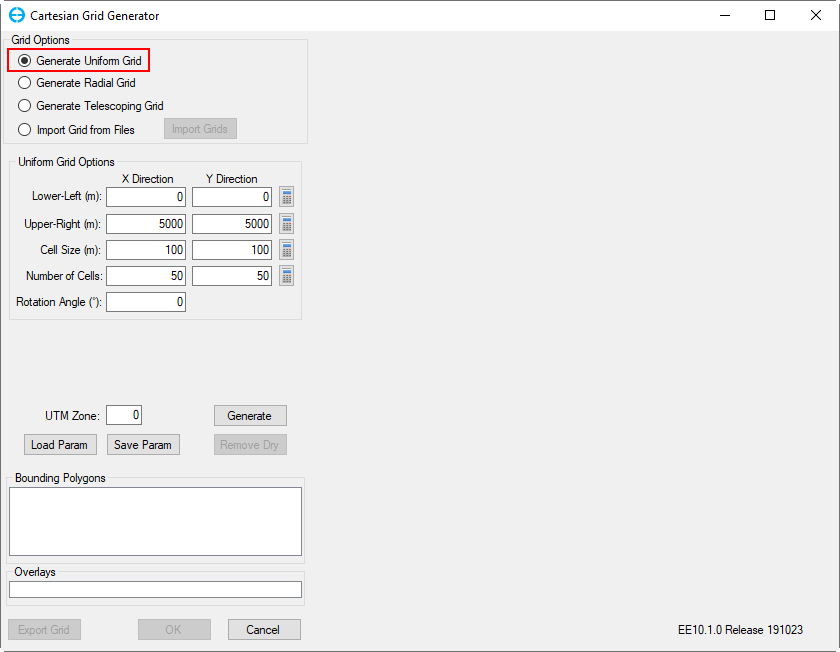
2. Click New Model icon: on the main menu of the EE interface. The Cartesian Grid Generator frame appears shown in Figure 2-1
3. In Grid Options, select Uniform Grid.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Figure 2-1. Generate EFDC Model form.
...
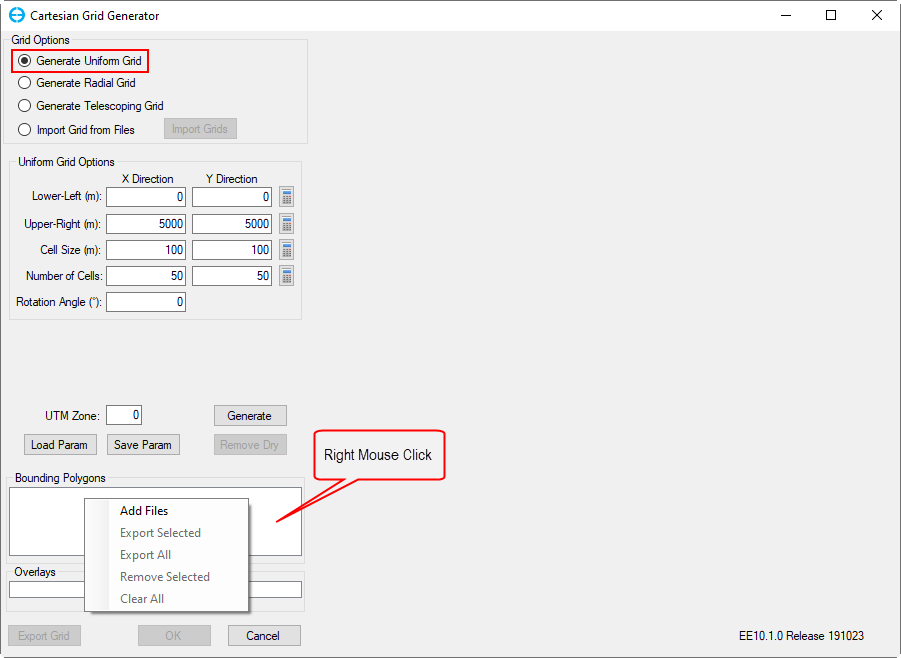
4. RMC (Right Mouse Click) on the Bounding Polygons blank to open a pop-up menu. In the pop-up menu, select Add Files to browse the polygon file. The land-boundary of the lake will be loaded here.
| Info |
|---|
The polygon file for this model is "Outline.p2d" and can be found in Data/Bathymetry folder of the Demonstration Models provided above. |
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Figure 2-23. Add polygon file
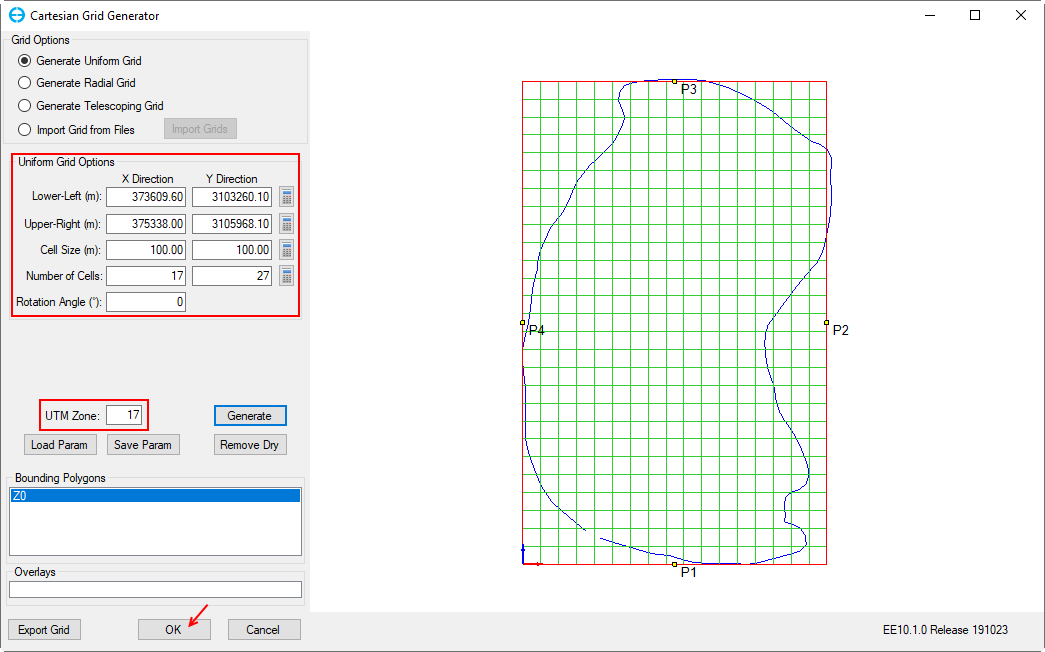
5. With the polygon file loaded, the X-Y Directions for the corners of the models are automatically defined. The user can also adjust the Cell Size and Number of Cells in Uniform Grid Options.
In this example, enter cell size is 100x100m for the Cell Size (m) then click the calculator symbol for the Number of Cells.
Anchor Figure 4 Figure 4
Figure 2-34. Loaded polygon file
6. If the user adjust any options in Uniform Grid Options they must click the Generate button so that EE can generate the changes.
...
9. Click OK button to finish grid generation. An overview of the created grid is shown in the General tab (Figure 2-45).
10. Save the model by selecting the Save button and create a new directory.
Anchor Figure 5 Figure 5
Figure 2-45. Grid information from generated model.
...
3 Assigning the Initial Conditions
This section will guide you on how to assign the initial conditions, such as the bathymetry, water level, and bottom roughness.
3‑1Anchor Figure 6 Figure 6
Figure 6. Assigning initial conditions.
3.1 Assigning the Initial Bathymetry
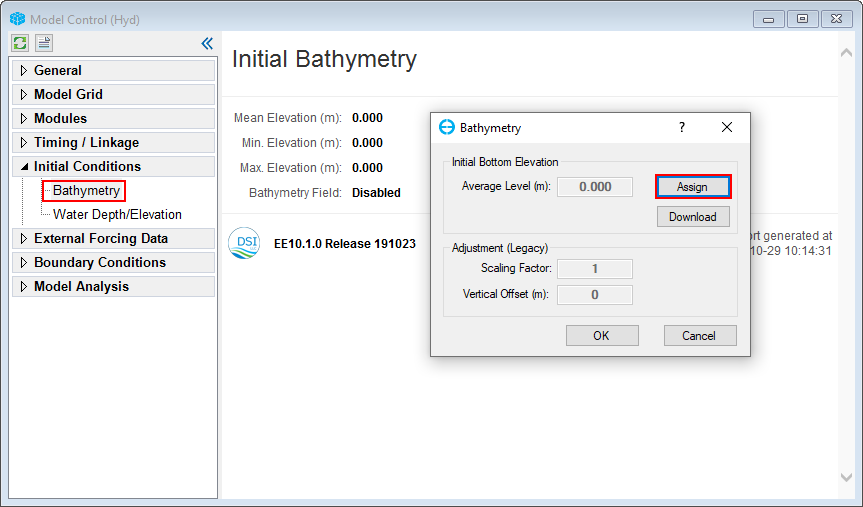
1. Select the Initial Conditions tab and right mouse click (RMC) on the Bathymetry sub-tab. A new Bathymetry form will appear. In that form, click on Assign to define bathymetric value.
Anchor Figure 7 Figure 7
Figure 3‑27. Assigning bathymetry conditions.
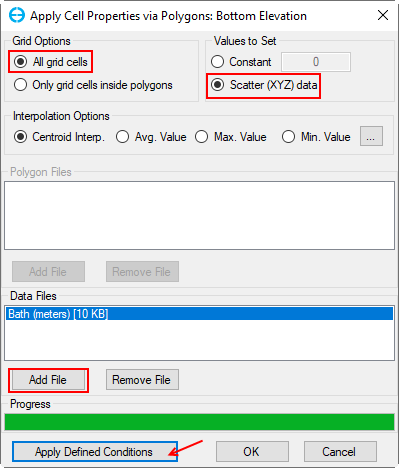
2. The area the user wants to assign the bathymetry data to is set by a poly file. In this case, choose All grid cells
3. The data for bathymetry values are assigned by “Bathymetry.dat” file in Bathymetry folder . This bathymetry file is simply an xyz format.
4. Choose Scatter (XYZ) data and then Add file to browse for “Bathymetry.dat”.
Anchor Figure 8 Figure 8
Figure 3‑38. Assigning bathymetry.
5. After adding the data file, click to on the Apply Defined Conditions button to make your changes take effect before selecting the OK button.
Anchor Figure 9 Figure 9
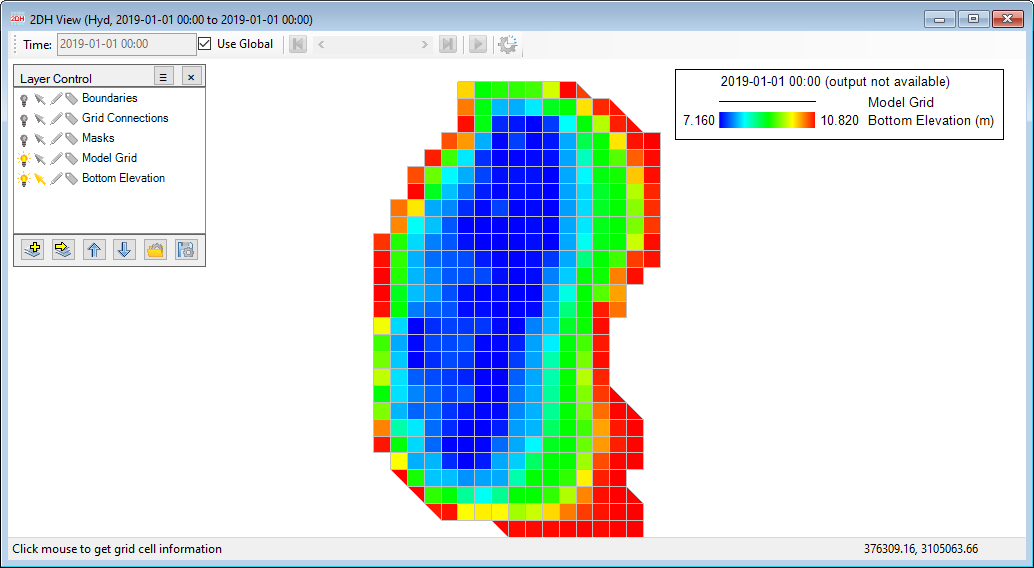
Figure 3‑49. 2DH View of bottom elevation after assigning bathymetry.
...
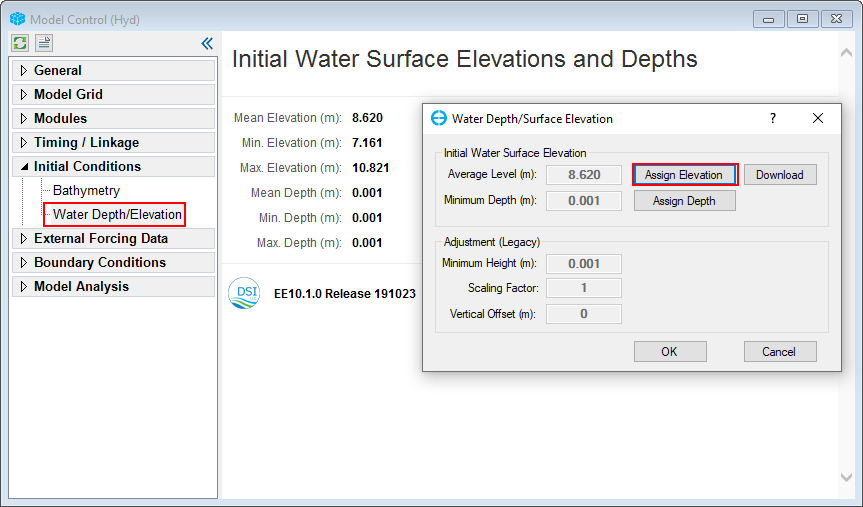
1. RMC on Water Depth/Elevation button then Click click Assign Elevation button (Figure 3-5)10)
Anchor Figure 10 Figure 10
Figure 3‑510. Assigning water depth/surface elevation.
...
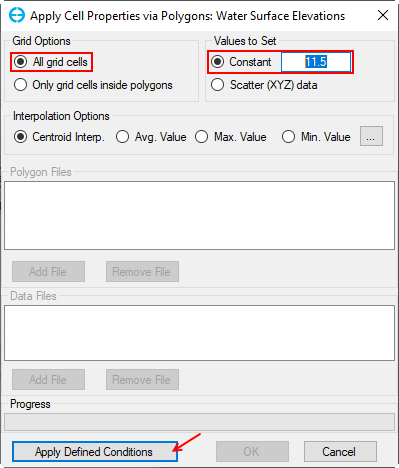
2. Select Constant to assign a constant water surface elevation of 11.5 m in the Constant box. (Figure 3‑611).
Anchor Figure 11 Figure 11
Figure 3‑611. Assigning water surface elevation (use constant option).
...
3. After selecting this option for assigning water surface elevation, click Apply Defined Conditions button, then click the OK button to finish.
...
This section will teach you how to prepare the boundary conditions and assign them to the model cell configuration. In this Lake 2D case, there are two flow boundaries; one is runoff inflow to the lake, and the other is outflow through a gate. Thus, we should prepare two-time series of inflow and outflow boundaries. In other cases, the number of time series for boundary conditions might be much more, such as those for hydraulic structures, pressure boundaries, or include time series for temperature, salinity, and water quality boundaries also.
4.1 Set Time Series
To set the boundary time series take the following steps:
1. Select the External Forcing Data tab. (Figure 4‑112)
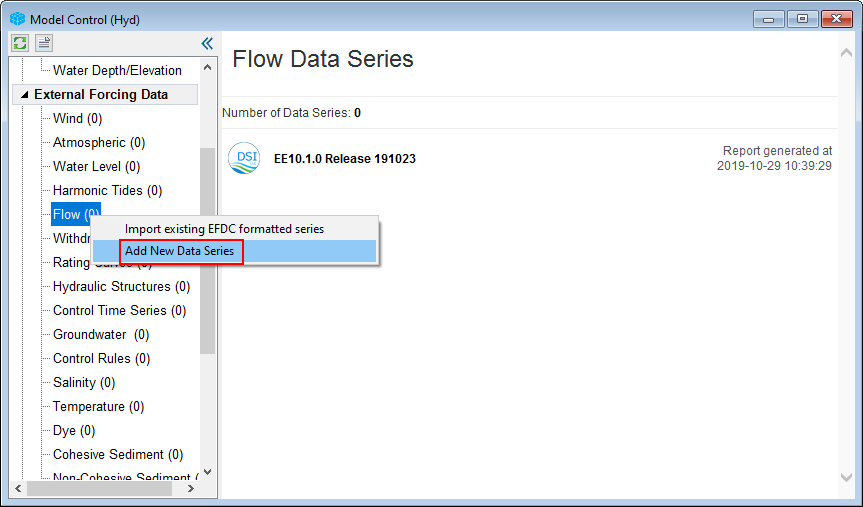
2. RMC on Flow button and select Add New Data Series to edit the flow boundary. (Figure 4‑1)13)
Anchor Figure 12 Figure 12
Figure 4‑112. Create flow time series.
...
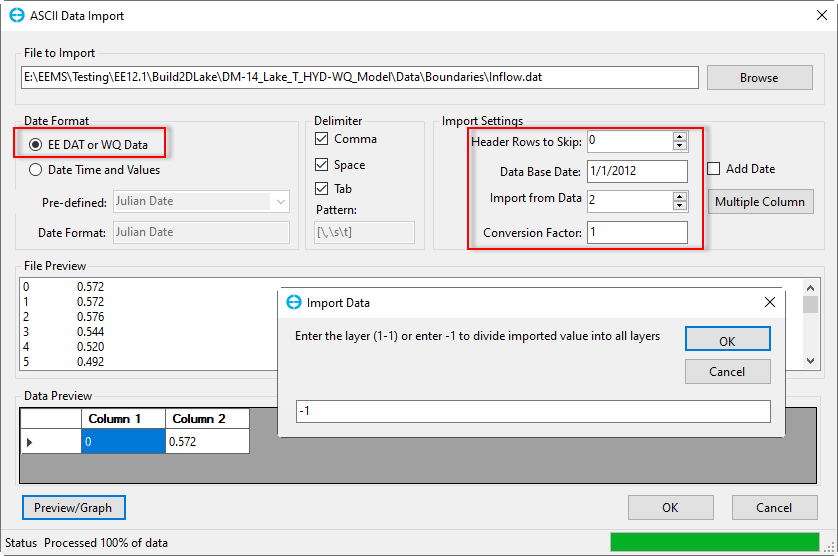
(4) Click OK in the Import Data window to close the form and finish importing data (Figure 4-313).
(5) Save the model
Anchor Figure 13 Figure 13
Figure 4‑213. Import flow time series.
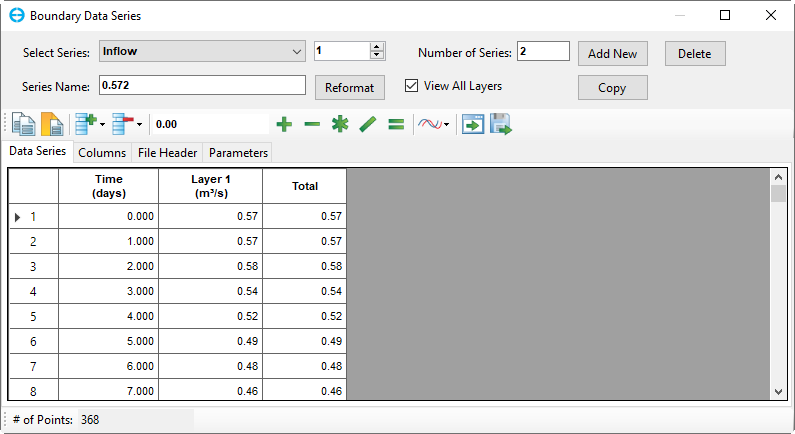
Anchor Figure 14 Figure 14
Figure 4‑314. Data series: Inflow.
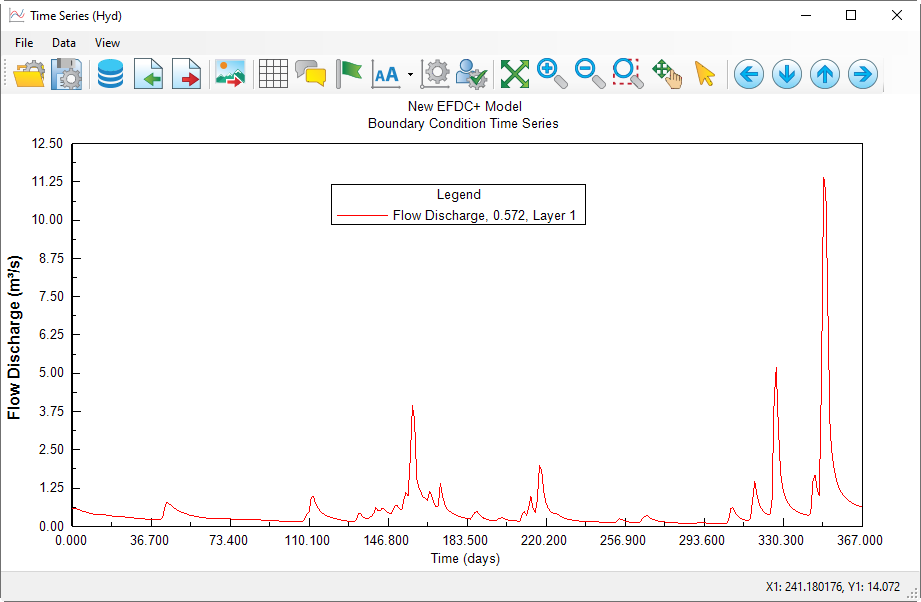
6. Click to the View Time series plot icon to view the current time series.
Anchor Figure 15 Figure 15
Figure 4‑415. Time series plot of inflow.
...
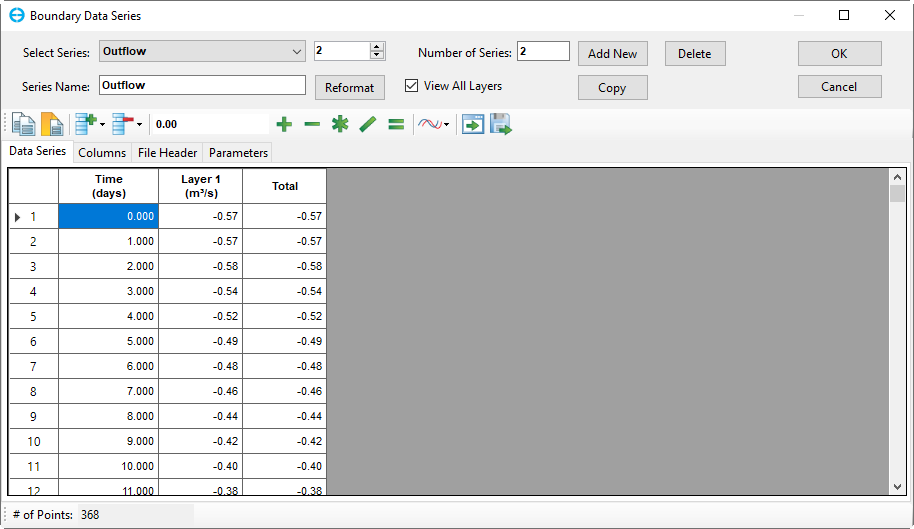
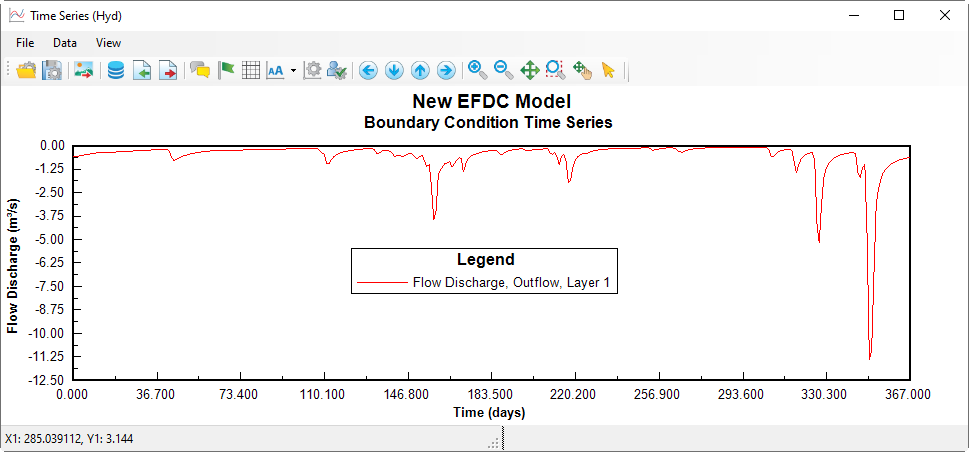
8. Repeat Step 5 to import “Outflow.dat" to the model (Figure 4‑516). The time series plot of outflow is shown in Figure 4-6.17.
Anchor Figure 16 Figure 16
Figure 4‑516. Data series: outflow.
Anchor Figure 17 Figure 17
Figure 4‑617. Time series plot of outflow.
...
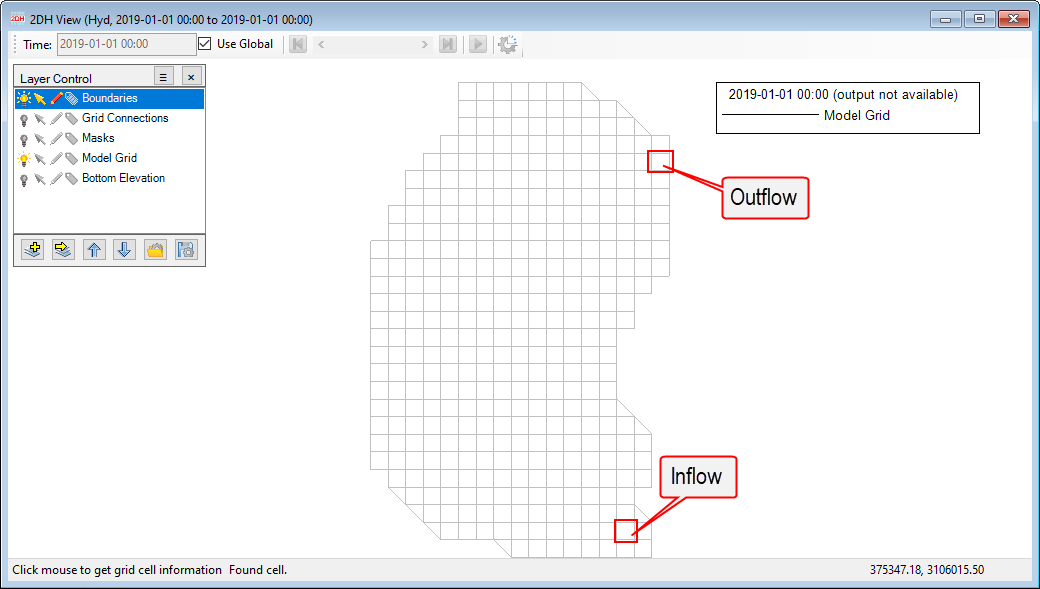
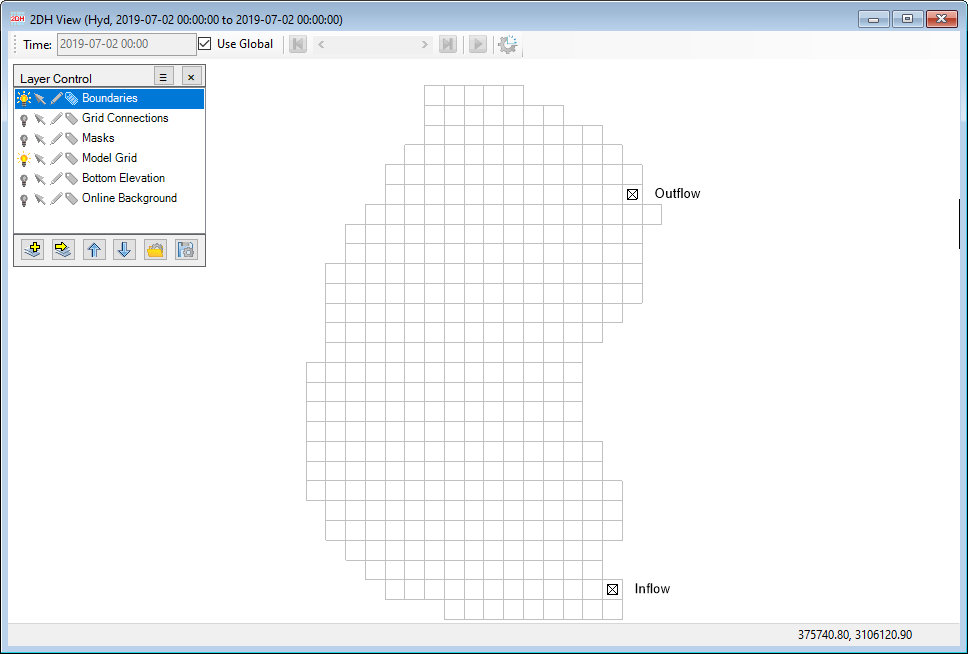
After completing the above steps, the user has prepared all the required boundary time series. Now, we will assign these boundary time series to the model cells. Figure 4‑7 18 shows the location of inflow and outflow for this lake case. Thus, we have to assign these cells with associated time series for in/outflow prepared in the previous session.
Anchor Figure 18 Figure 18
Figure 4‑718. Locations of inflow and outflow for the lake.
...
1. Click the 2DH View icon on the main form of EE (Figure 1‑11).
2. Choose Boundaries in the Viewing Layer Control .
3. Enable Edit grid by turn turning on the icon (seeFigure 4‑819)
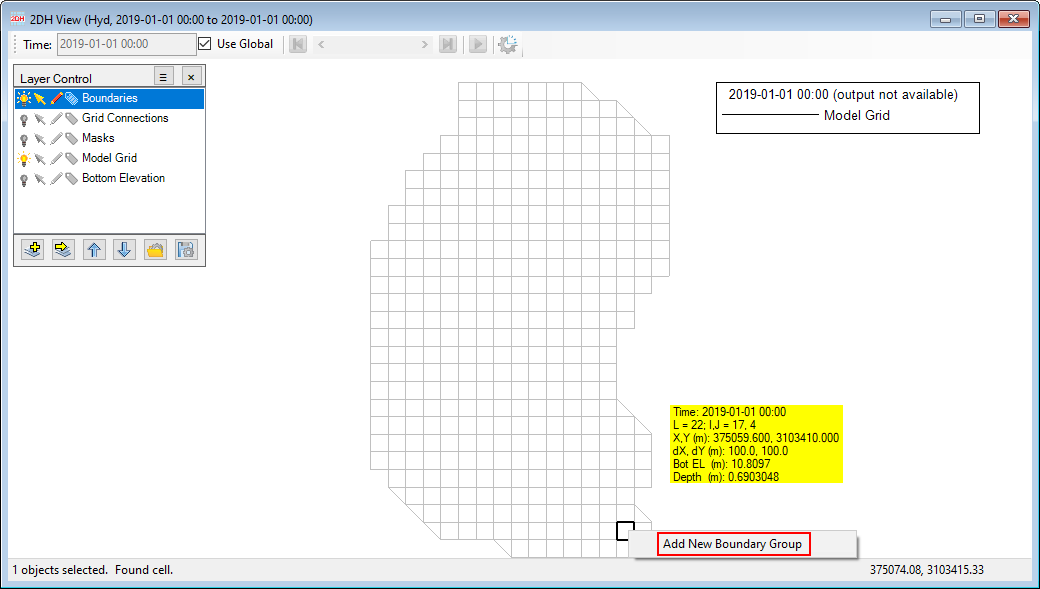
4. RMC on the inflow location cell and select Add New Boundary Group Group (Figure 4‑920)
Anchor Figure 4-819 Figure 4-819
Figure 4‑819. Enable to edit Boundaries layer.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Figure 4‑920. RMC on the inflow cell to add a boundary condition.
...
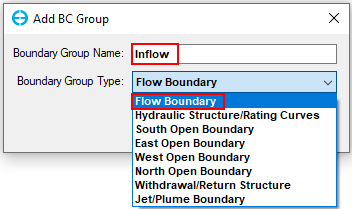
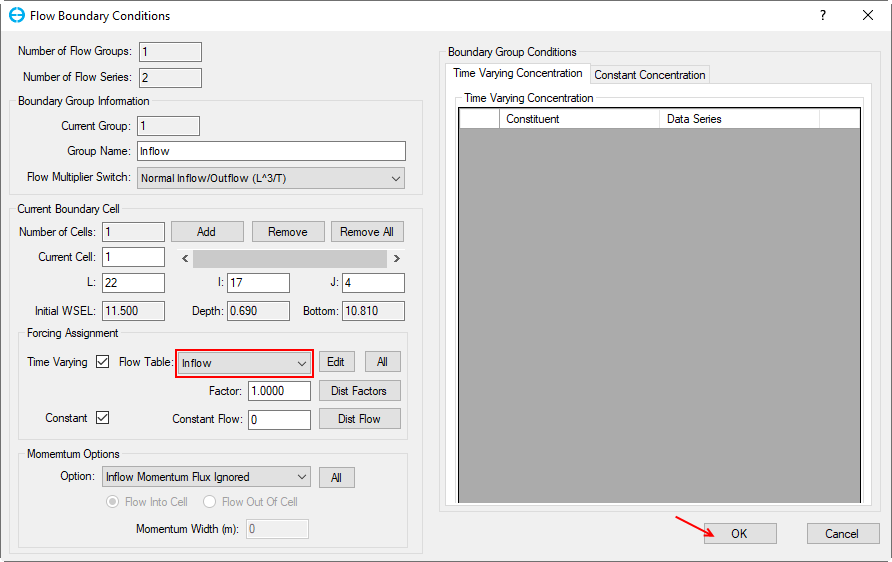
5. Enter the Boundary Group Name by typing “Inflow” and select boundary types (Figure 4‑1021). Then click OK button, the Flow Boundary Conditions form appears , in the Forcing Assignment frame, select "Inflow" for Flow Table (3407876Figure 22), then click OK button.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Figure 4‑1021. Enter Boundary Group Name and select Boundary Group Type.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Figure 4‑1122. Assign the corresponding time series.
...
6. Apply the same process for assigning the outflow boundary cell. Figure 4‑12 presents 23 presents the boundary conditions after assigning the inflow and outflow boundaries.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Figure 4‑1223. Inflow and Outflow boundaries assigned.
...
2. Enter the duration of start/ end of the simulation. Note that the boundaries time series should always cover this simulation duration period, otherwise, the model will not run.
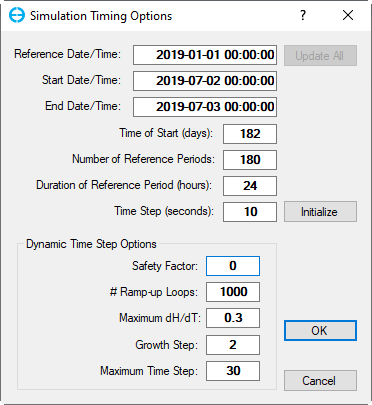
3. Enter the Time of Start, Number of Reference Periods, Duration of Reference Periods and Time Step as 3407876 Figure 24. These values are explained in Table 2 of Build a 2D Lake Model with EE8.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Figure 5‑124. Model run time.
4. RMC on Linkage button and set Link EFDC Results to EFDC+ Explorer and set Linkage Output Frequency to 60 minutes. This means that EFDC will record the output every 60 minutes for the display of the model results in the EE. (Figure 5‑2). Note that a smaller output frequency will create a larger output file.
...